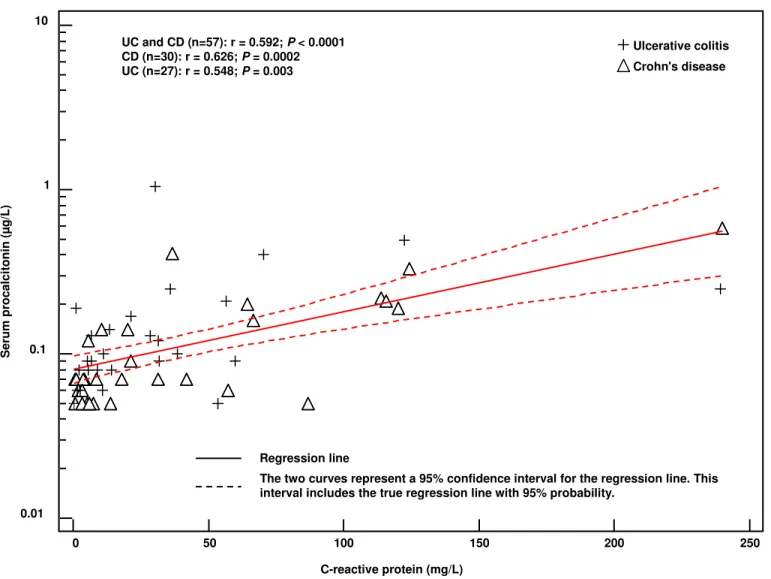
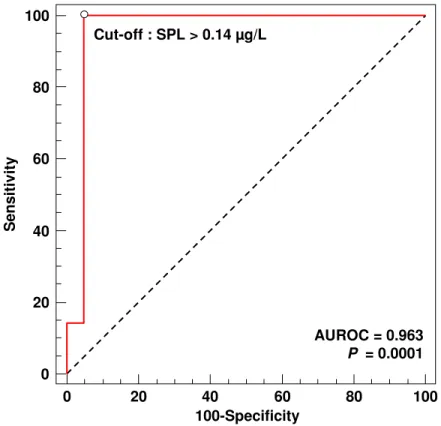
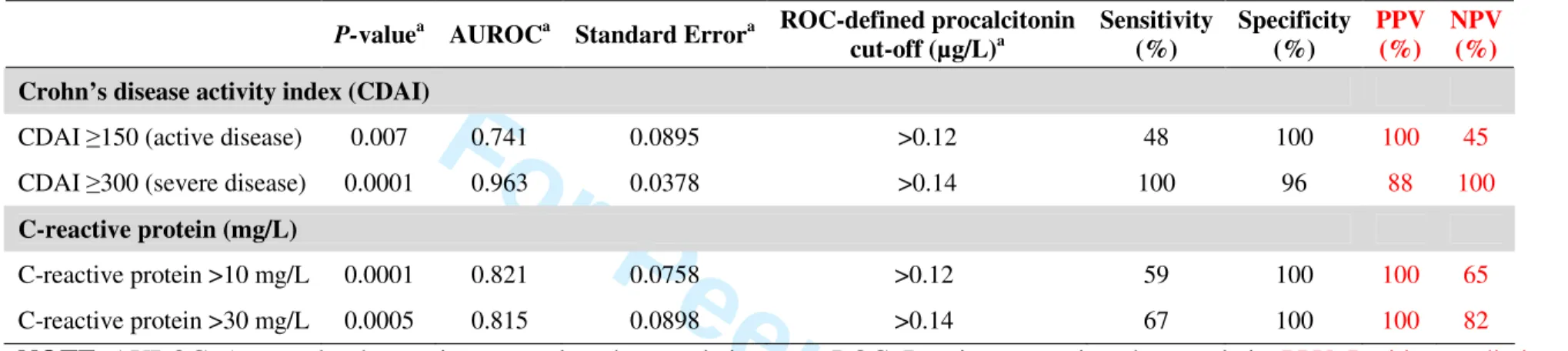
Additional benefit of procalcitonin to C-reactive protein for assessing disease activity and severity in Crohn's disease: Procalcitonin in inflammatory bowel diseases
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
This paper presented two case studies from the automotive domain that relies on mobile communication technologies and mobile ad-hoc networks to improve the
Macroscopic evolution of mechanical and thermal energy in a harmonic chain with random flip of velocities.. Tomasz Komorowski, Stefano Olla,
The Drude-Lorentz model fits (dashed line) to the real and imaginary (inset) parts of the in-plane optical conductivity of MoTe 2 (solid line) decomposed into the narrow and broad
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE WEB.
The aim of this study was therefore to assess the risk of dysplasia or cancer among IBD patients undergoing intestinal resection for a colorectal stricture without
In univariate analysis, clinical disease activity and the persistence of systemic inflammation, diabetes, dyslipidemia and hypertension were significantly associated with an
Our objective was to assess the frequency of ATG16L1 (T300A) and IL23R (L310P) variants in Moroccan IBD (Crohn ’ s disease and Ulcerative Colitis) patients and to evaluate a
Top panels (a, b, c, and d) present the hypothetical causal diagrams and bottom panels (e, f, g, and h) present the corresponding scatterplots of B as a function of g in the