Cereal yield gaps across Europe
Texte intégral
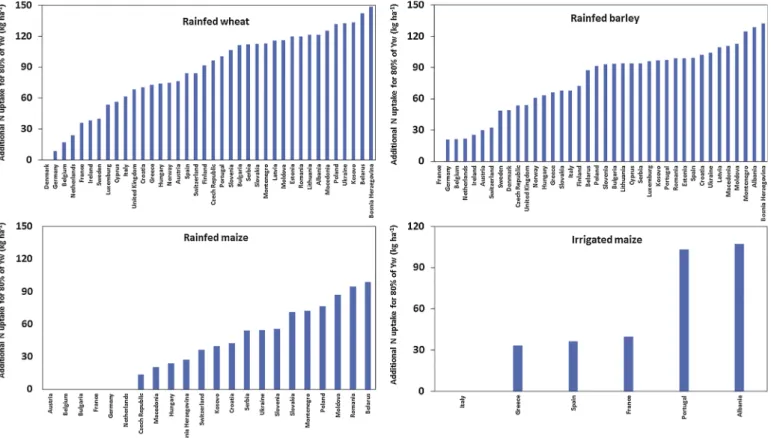
Figure


Documents relatifs
Eleven hybrid combinations developed by three line systems with two standard check varieties were evaluated in two rice growing seasons in 2014 and 2015 at the
4.2 Estimates of standard heterosis for rice hybrids: Standard heterosis computed over check varieties (Giza 179 and Sahel 108) for nine traits revealed that heterosis
5 Linear relationships between regional mean yield of feed barley and Shannon index describing cultivar diversity in the south-west and central-east regional groups in 1998
Interrelationships of total land equivalent ratios and total grain yields (kg ha −1 ) of wheat and faba bean grown under mixed intercropping.. Competition among
The aim of this review is to explore some of the existing methods to assess potential grain yield, the size of the gap between average and rainfall-limited potential yield and
Simulation of winter wheat yield and its variability in different climates of Europe: A comparison of eight crop growth models... nuscript Manuscrit d’auteur / Author manuscript
In this study, we analyzed data from a 50 year long-term field ex- periment to assess (i) the change of climatic parameters, wheat yield and soil organic carbon (SOC) content; (ii)
A PSU is a relatively homogenous unit in terms of its relative productivity (yield) each year and the temporal stability of this relative yield. The overall goal is to develop