Extension of the SAEM algorithm for nonlinear mixed models with 2 levels of random effects.
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
The main drawback of the previous approach is that the precomputation step will mesh the whole parameter domain, whereas SAEM algorithm will concentrates on particular areas of
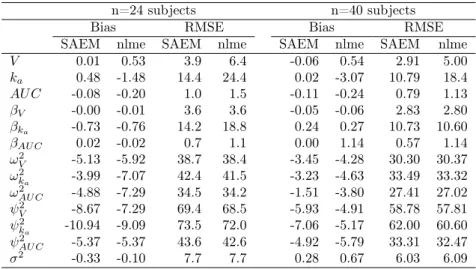
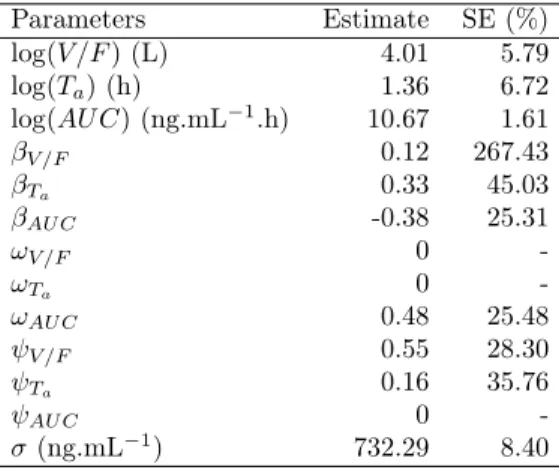
Test for 92 populations of 1000 individuals: Results (from Monolix) and errors for the mean parameters of the population.. Column E1 refers to a population
is chosen in order to increase the accuracy of the meta model by a factor 100. After this whole process, only 22 points have been added in the basis, while the KSAEM run made
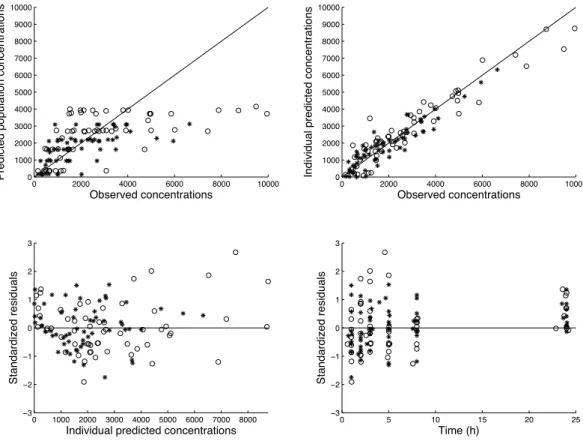
Since we obtained the same results as the exact NLMIXED method, our method seems to be adapted and efficient in maximum likelihood estimation in the general class of the
In summarizing time-to-event data, there are two main functions of interest, namely the survival function and the hazard function. The actual event time t can be regarded as the
Since the individual parameters inside the NLMEM are not observed, we propose to combine the EM al- gorithm usually used for mixtures models when the mixture structure concerns
Note that generating random samples from p i (ψ i |y i ) is useful for several tasks to avoid approximation of the model, such as linearisation or Laplace method. Such tasks include
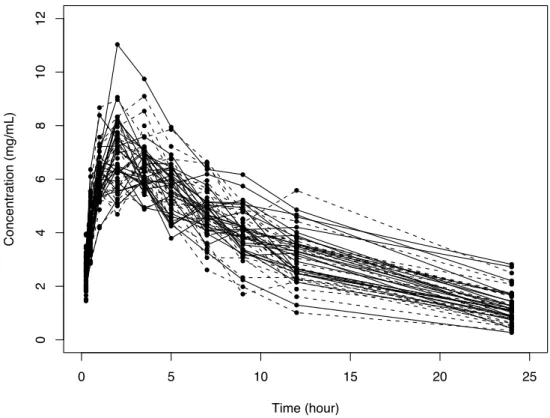
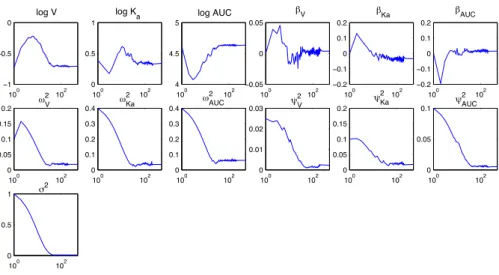
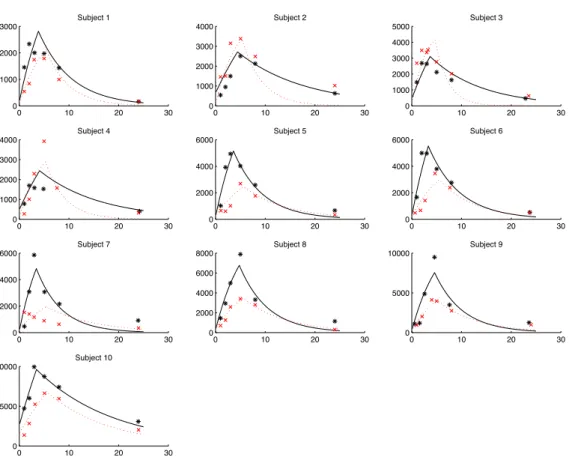
We simulate data sets using the bi-exponential model for HIV dynamics proposed by Ding and Wu (2001), and evaluate the statistical properties of the extended SAEM parameter