Predictive factors for incident musculoskeletal disorders in an in-plant surveillance program.
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
Petersen T, Kryger P, Ekdahl C, Olsen S, Jacobsen S: The effect of McKenzie therapy as compared with that of intensive strengthening training for the treatment of patients with
2.1 Risk factor: Manipulation of heavy loads 15 2.2 Risk factor: Work with high force exertion 18 2.3 Risk factor: Working in unfavourable body postures 19 2.4 Risk factor:
To determine if occupational factors were associated with the outcome in workers with UEMS symptoms or disorders, we used data from the repetitive task survey performed in 1993 1994
Based on the results of this previous study, this paper aims to (i) assess the combined effect of occupational biomechanical (e.g., high physical exertion) and psy- chosocial (e.g.,
The aims of this program are: (i) to estimate the incidence and prevalence rates of the main MSDs in the general population of a French region and their time trends according to age,
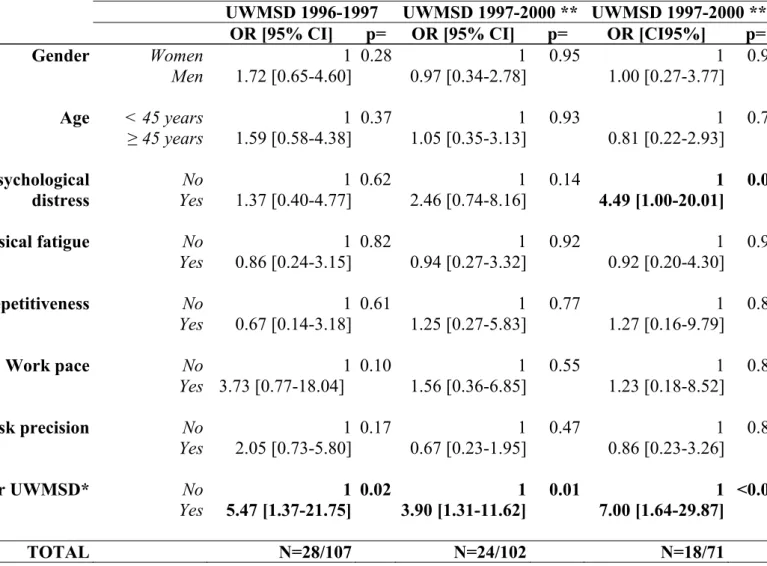
(*) Subjects with no missing value for the risk factors in the multivariate model; Number of subjects excluded from analyses because of missing values: 129 men and 112 women; OR,
Exposure in relation to work status and occupational risk factors was assessed with a self-administered questionnaire, and was categorized according to vibration exposure
phism), VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) EGF (epidermal growth factor), FGF1 (fibroblast growth fac- tors 1), FGF2 (fibroblast growth factors 2), RA (Rheuma- toid

