Acousto-electrical speckle pattern in Lorentz force electrical impedance tomography
Texte intégral
Figure
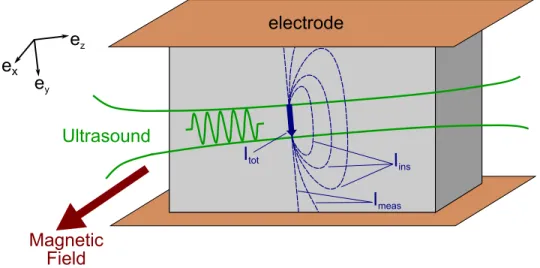
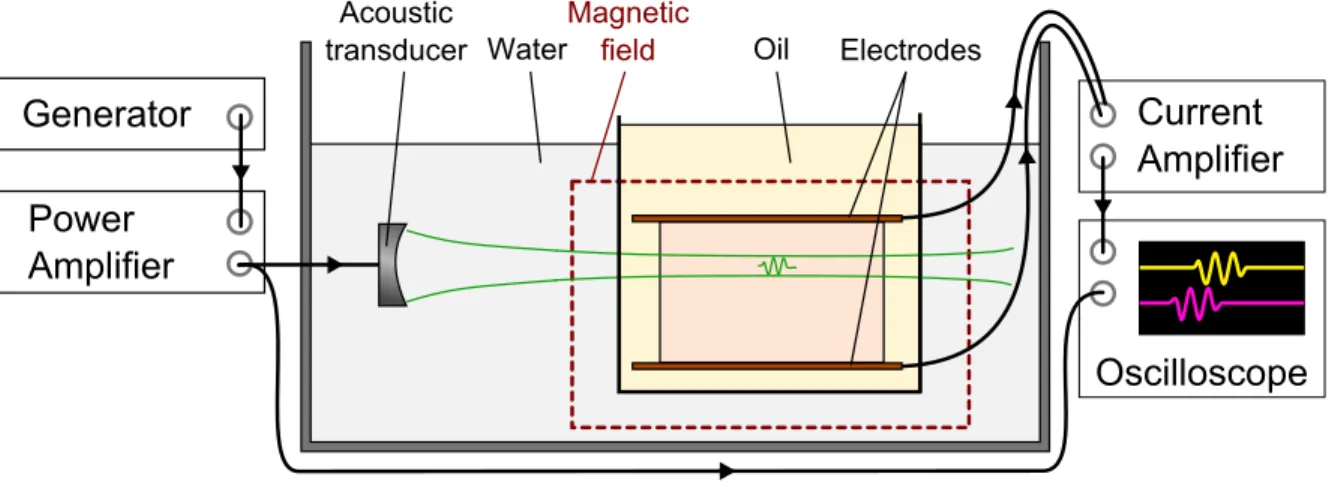
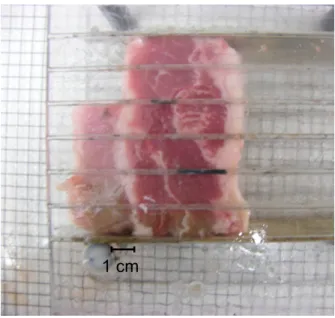
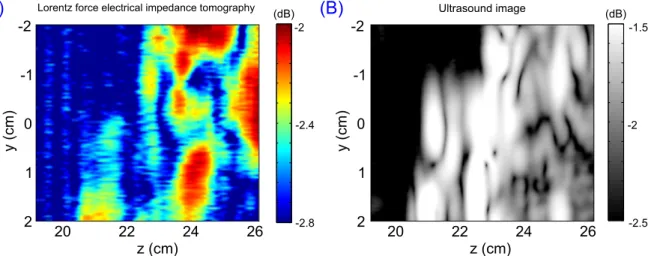
Documents relatifs
The conversion over the powder samples is lower than that of the platelets indicating that there might be diffusion limitation inside the pellets, as the pellet size (250 m)
Perceptually weighted model estimation (PNTF) In this study, instead of the ML approach (7), we propose to estimate the model parameters through a perceptually weighted NTF, which
Wives of maîtres ouvriers involved in piquage d’once, tireuses de cordes working illegally on the loom, embroiderers claiming their unpaid wages: these women developed a variety
In order to get a better understanding of how the TNBCtype tool can be used for TNBC subtype prediction, I am going to cluster a large TNBC dataset, using the clustering methods
This paper aims to fill that void: we investigate the existence of second order derivative of the state u with respect to perturbations of the shape of the interface ∂ω, then we
We explain how to build invisible isotropic conductivity perturbations of the unit con- ductivity in the framework of the point electrode model for two-dimensional electrical
Several numerical tests show that the method is able to detect the presence and location of the inclusions, in many cases where the diffusion coefficient depends nonlinearly on
To solve this nonlinear inverse problem, we first make use of a virtual potential to relate explicitly the current measurements to the conductivity distribution and the velocity of