A posteriori error estimates for combined finite volume-finite element discretizations of reactive transport equations on nonmatching grids
Texte intégral
Figure

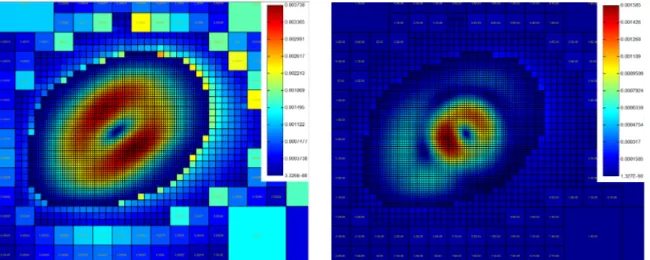
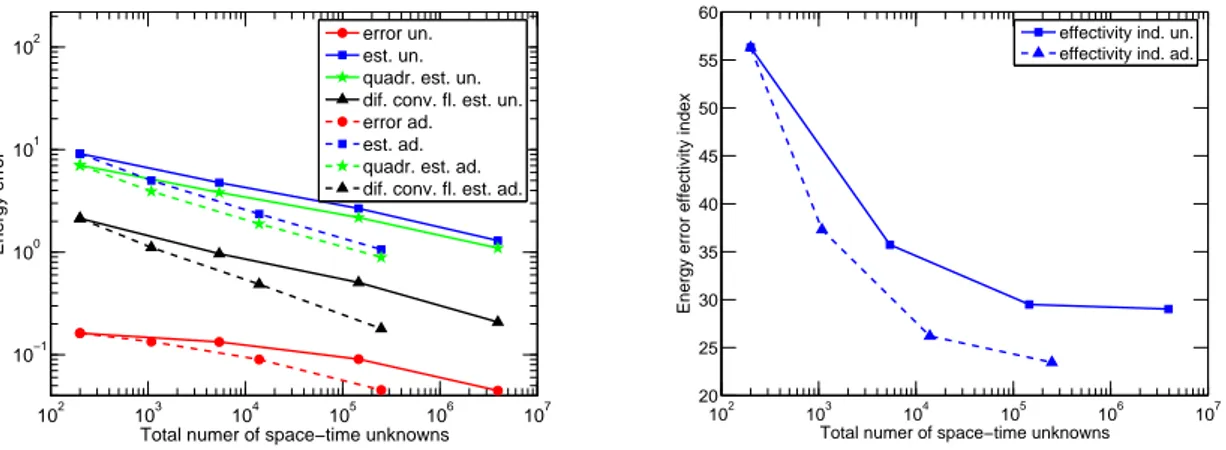

Documents relatifs
The upwind scheme (3.3a)–(3.3b) guarantees stability in the convection-dominated case, but the additional a posteriori error estimator η σ given by (4.7) is unfortunately not
Le souffle continu du ventilateur Dans la nuit noire traversée de rouge De jaune.. Être dans ce lit, ce
In Section 2 , we present and analyze the positive finite volume scheme discretizing the convection- diffusion model ( 1.1 )-( 1.4 ). More specifically, we first describe the
Key words: degenerate parabolic problem, convection–diffusion–reaction equation, inhomoge- neous and anisotropic diffusion, convection dominance, nonmatching grids, finite
convection-diffusion equation, combined finite element - finite volume method, Crouzeix-Raviart finite elements, barycentric finite volumes, upwind method, sta-
Wellknown discretization methods are finite differences, finite volumes and finite elements. The mathemat- ical study of convergence is quite wellknown in the case of
This scheme may be characterized by the fact that the diffusion term in (1.1) and (1.7) is approximated by piecewise linear Crouzeix − Raviart finite elements, and the convective term
We observe that the convergence rate is the same and that Scheme 1 leads to a value of ∆t n two orders of magnitude larger than the one used for Scheme 2 in order to make the