Coupling, Reinforcement, and Speciation
Texte intégral
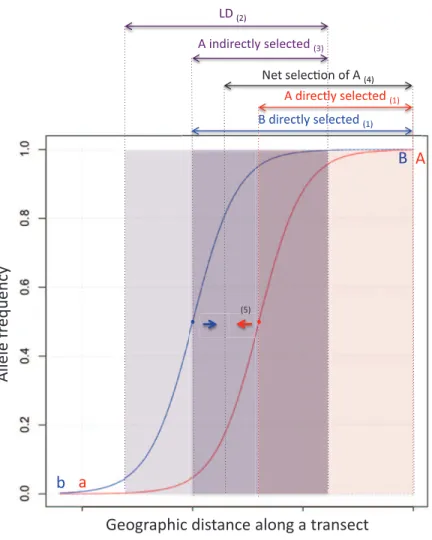
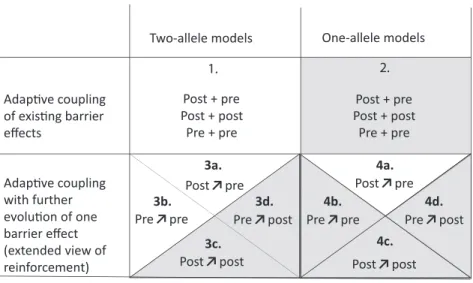
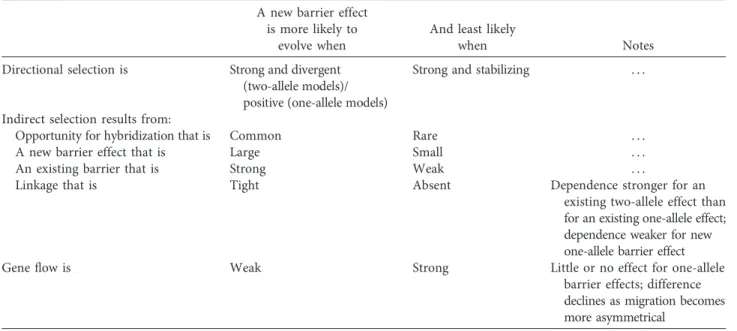
Figure

Documents relatifs
LENDER (1951) la récolte aux environs de Strasbourg. — Localisation des stations étudiées. On l'observe en particulier sous les pierres et sous une faible épaisseur
Les volumes antérieurs de cette publication sont également disponibles sur microfilm
Although we found reduced coffee suitability and bee species diversity for more than one-third of the future coffee-suitable areas, all future coffee-suitable areas will
Although we found reduced coffee suitability and bee species diversity for more than one-third of the future coffee-suitable areas, all future coffee-suitable areas will
If spin orbit coupling in the absorption band is the dominant spin mixing mechanism the sign of the pumping effect will be the same everywhere in the absorption band, if some
The current enhancement factor peaks when the absorption maximum of rr-P3HT crosses the (1,0) and (1,1) modes of the hexagonal plasmonic array (Figure 2d) and undergoes
We presented the VS task for refining the final grasping pose prior to grasp to address the challenges linked to final gripper pose, reported in literature related to transfer
For Exp3 ‐ a and Exp3 ‐ b, even if the average melt rate is higher, a change in the melt distribution has the effect of increasing the velocity field just downstream of the
