Gradient-Based Algorithm with Spatial Regularization for Optimal Sensor Placement
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
Existing algorithms are mainly based on formulating an optimization problem once the sets of all possible ARRs have been gen- erated, considering all possible candidate
Given a structural model, a set of candidate sen- sors to be installed in the system and a cost asso- ciated to each sensor, the problem to be solved in the present paper can
The novelty is that binary integer linear programming is used in the optimization problem, leading to a formulation of the detectability and isolability specifications as
The optimal sensor placement problem was solved for increasing number of ARRs (i.e., increasing sizes of the Full ARR Table and the Full Fault Signature Matrix were considered)..
Those consist in the maximum avoidance of the excluded zones, not exceeding the maximum number of sensors desired in a solution (being able to be fixed with
It is important to point out that both the fixed communication cost and the consumption rate depend on whether the particular sensor spends the period awake or asleep: sleeping
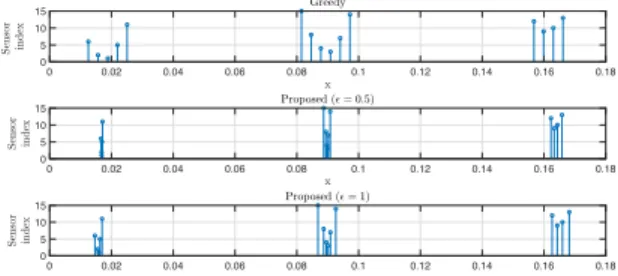
Finally, we present numerical results showing the superior robustness of the proposed approach when compared to standard sensor placement criteria aimed at interpolating the
• Stopping condition redesigned (integrated with the exploration/exploitation strategy and based on the interest of the search and diversity of new solutions). ACOv3f: algorithm