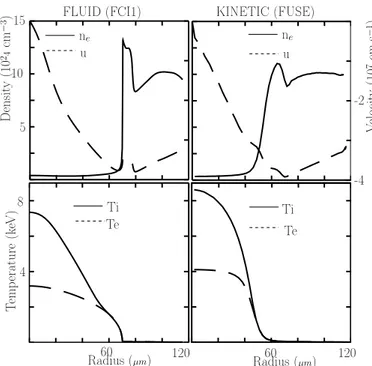
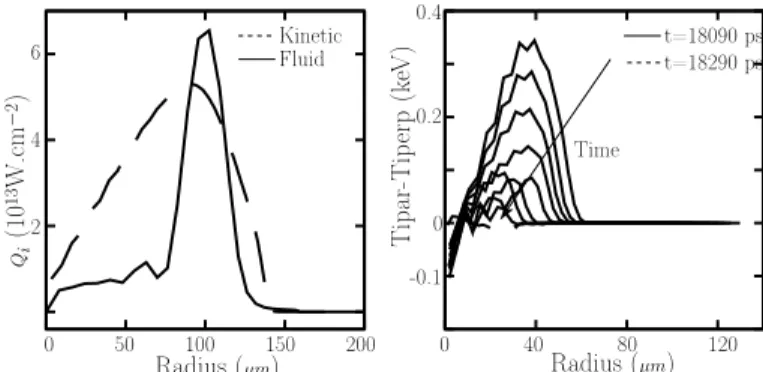
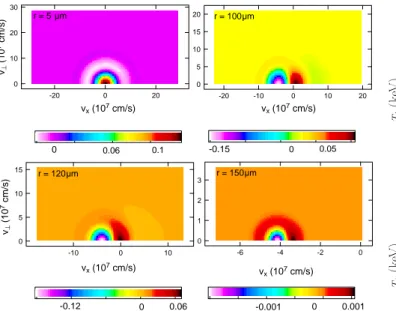
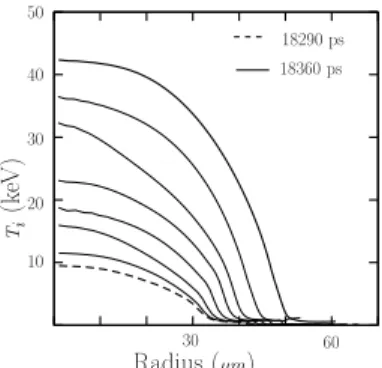
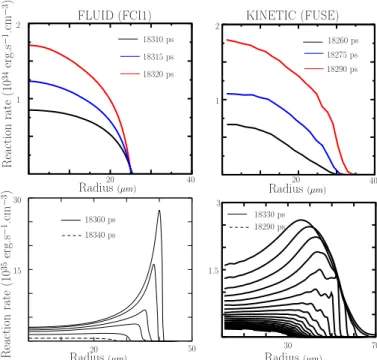
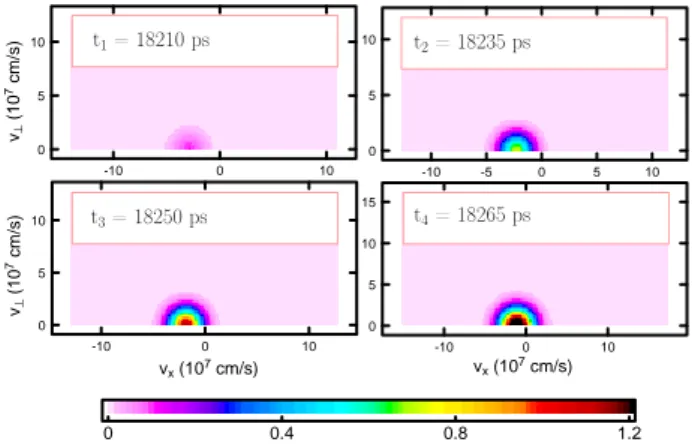
Ion kinetic effects on the ignition and burn of ICF targets
Texte intégral
Figure
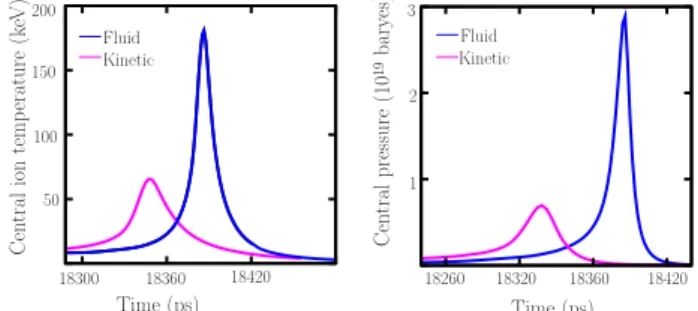
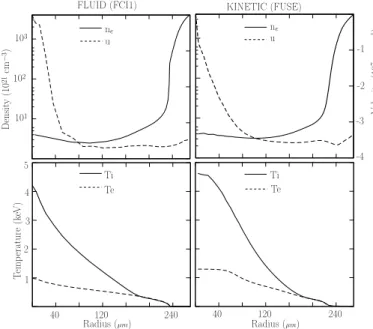
Documents relatifs
Effects of the load duration and sample thickness: (a) on the location of the delamination, and (b) on the ultimate tensile stress... Barker L M and Hollenbach R E 1972
We study coherent nonlinear kinetic plasma structures at the foot of the Earth’s bow shock, whose typical size is somewhat larger than the electron Larmor radius and the ions
Using high frequency electric field mea- surements from the WIND satellite, we determine for the first time the wavelength of intense Langmuir wave packets that are generated
other crossings of similar shock structure shown in reference [23], when the second and third frequency band was observed, electrostatic noise with amplitude below 0.5
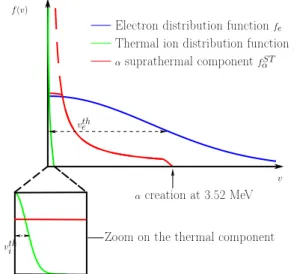
In these models, the VDF generally have (1) an isotropic Maxwellian core around the origin in the velocity space and (2) a highly asym- metrical halo population of suprathermal
The ionization rate coefficient of Ba and the electron density are determined by solving the space-dependent electron Boltzmann equation using the measured cathode fall voltage and
The shock wave polymerisation proceeds without any catalysts commonly used to initiate the process at normal conditions £2,4 1. The active centers are created by the shock wave,
Recently Kuzmin [8] studied transonic flow in a channel where a shock is formed due to a bend of the upper wall, while the sonic line arises due to an expansion corner of the