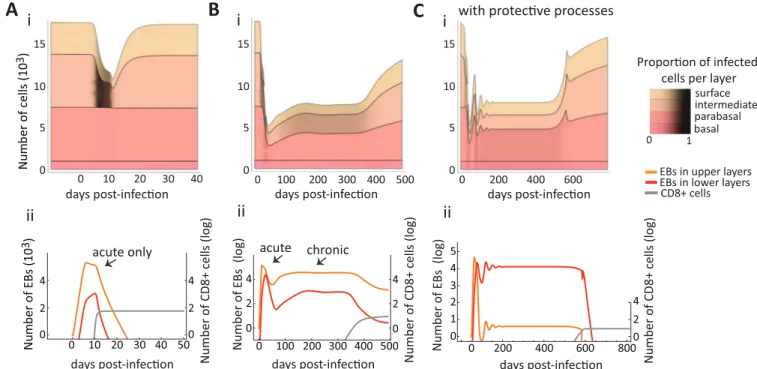
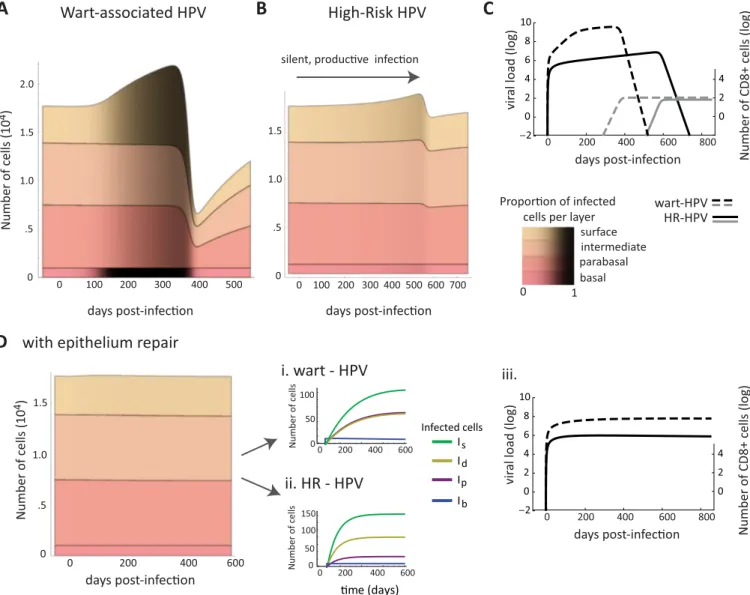
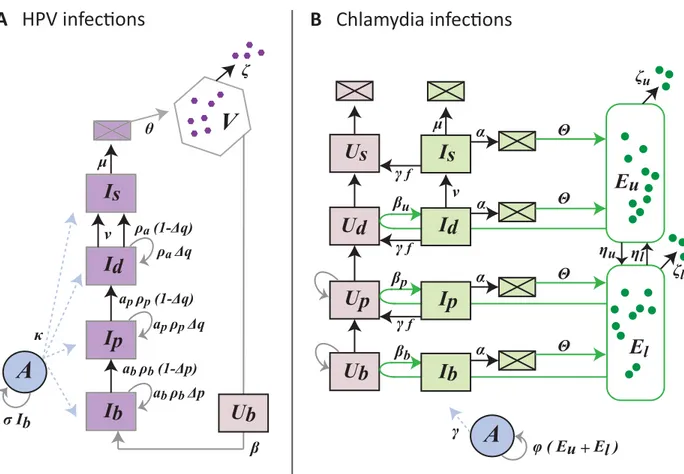
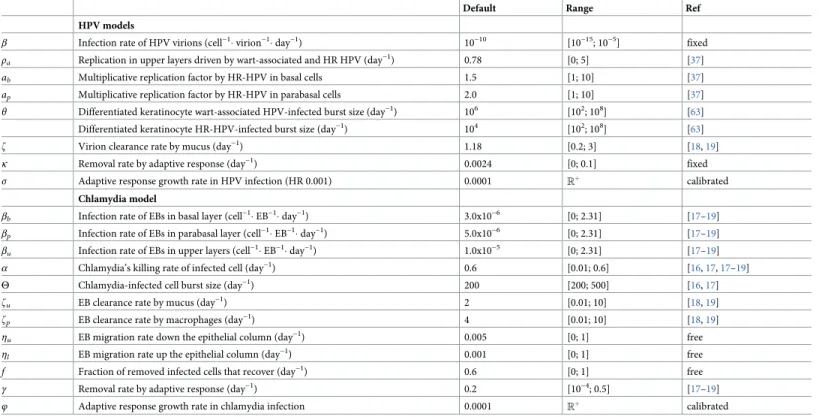
Epithelial stratification shapes infection dynamics
Texte intégral
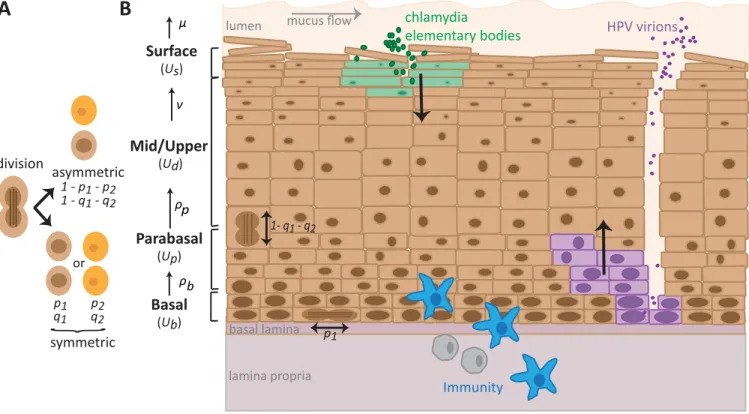
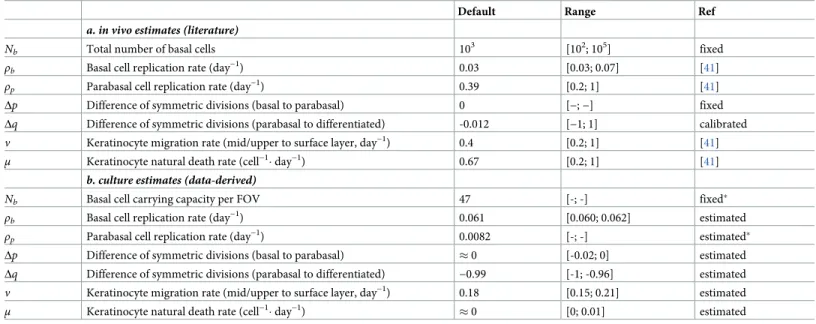
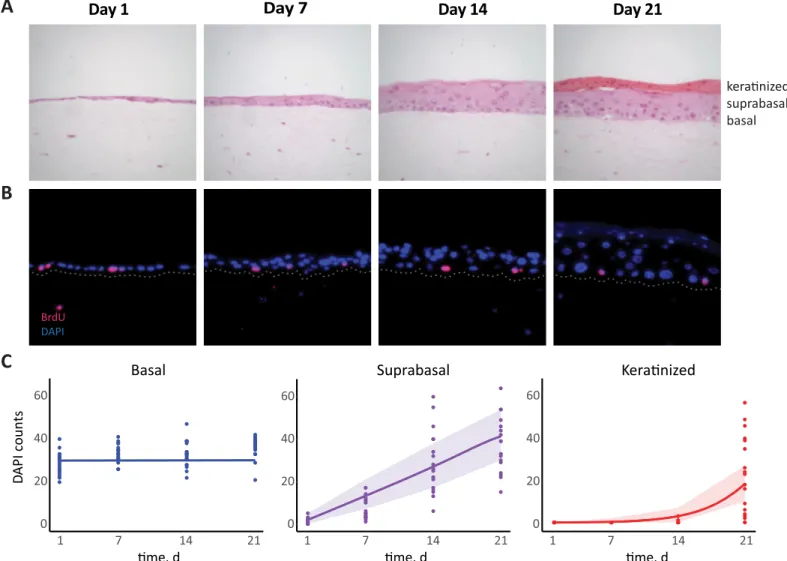
Figure

Documents relatifs
Monodisperse sequence-encoded poly(alkoxyamine amide)s were synthesized using an iterative strategy employing two chemoselective steps: the reaction of a primary amine with an
into a two-parameter deformation of zðkÞ, the elliptic zeta value at k, which obeys identities of modular type.. These identities are essentially equivalent to modularity in the
Mammary stem cells and normal breast development are regulated by the same signaling pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways, estrogen receptors and the
En se penchant sur le cas de quatre communes qui ont mis en place des manifestations autour de la route (Pougues-les-Eaux, Lapalisse, Loriol-sur-Drôme et Tourves), l’article
However, although we measured an increase of mitochondrial ROS production, a prominent depolarization of mitochondria in DJ-1 KO cells, and reduced mitochondrial connectivity, the
The changes induced by DN-MRTFA are globally inverse to those of DP-MRTFA, with significant decrease of the EMT and basal cell signatures, but less obvious changes of glycolysis
Here, we investigate the involvement of two tight junction-associated proteins, ZO-1 and GEF-H1 in the regulation of mechanical forces applied on adherens junctions and their
Here, in both cuboidal and columnar epithelia we have characterized a multicellular mechanism that coordinates completion of cytokinesis and de novo formation of SJ