Query and Predicate Emptiness in Ontology-Based Data Access
Texte intégral
Figure



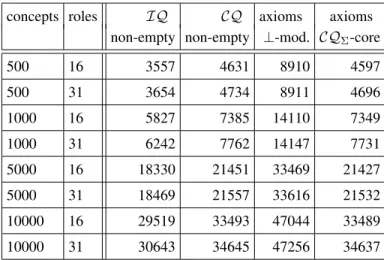
Documents relatifs
We study the data complexity of conjunctive query answering under these new semantics, and show a general tractability result for all known first-order rewritable ontology languages.
As a result, the TBox of the input ontology is represented by a set of TBox clauses, and the ABox of the input ontology is represented by a set of role assertions, ABox clauses as
The distinguishing feature of STARQL is its general stream windowing and ABox sequencing strategy which allows it to plugin well known query languages such as unions of
In fact, both the event ontology and the geographic ontology can be further divided into two cases, the automatic meaning the ontology is constructed automatically using
Since computing uniform interpolants for small signatures is much more computationally expen- sive as forgetting small sets of concept symbols, we performed the experiments only on
Given a query on the target ontology, our system uses a joint probability model to identify a maximal scoring, partial mapping that covers the target ontology entities mentioned in
We show that query answering can be distributed in a network of description logic reasoning systems in order to support scalable reasoning.. Our initial results
The complexity of the corresponding concept satisfiability problems without theories, which are equivalent to the satisfiability problems for the corresponding fragments of
