Finite-Time and Fixed-Time Input-to-State Stability: Explicit and Implicit Approaches
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
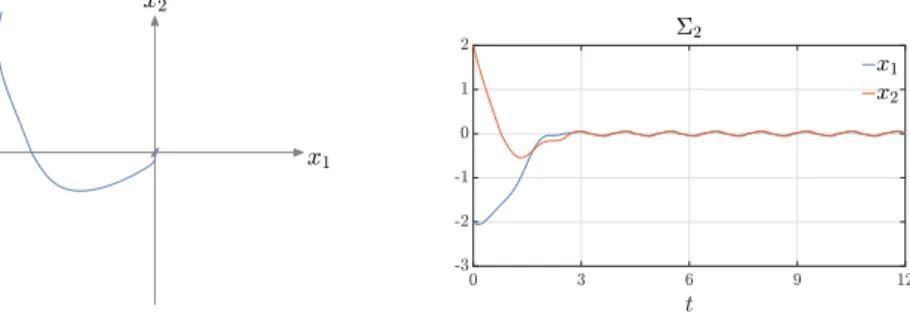
Using this theoretical framework new algorithms of finite-time and fixed-time stabilization for a chain of integrators and high order sliding mode control design are developed.. The
In this approach, the observer is designed firstly by studying the stability of the differential equation that describes the observation error, then, a nonlinear output injection
we show
Both properties, convergence time and ISS robustness, have been entirely developed using Lyapunov analysis, meaning that there exist tools such as finite-time, fixed-time and
It is a stochastic variance- reduced proximal-gradient type algorithm built on Stochastic Path Integral Differential EstimatoR (SPIDER), an algorithm known to achieve
Chapters 2 and 3 focus on theoretical contributions; the former presents necessary and sufficient conditions for fixed-time stability of continuous autonomous systems whereas the
Acramov._ Séléction préparation des jeunes footballeurs._ (Traduit par : A. _ ﻊﻴﺯﻭﺘﻟﺍﻭ ﺭﺸﻨﻠﻟ ﻕﻭﺭﺸﻟﺍ ﺭﺍﺩ.. ﻱﺭﻜﺫﻟﺍ ﺝﺫﻭﻤﻨﻟﺍ ﻲﻓ ﺔﻠﺜﻤﻤﻟﺍ ﺔﻴﻭﻁﻠﺴﻟﺍ ﺔﺴﺭﺎﻤﻤ ) ﺏﻷﺍ (
absence of an effect of the behavioral paradigm on the activity of 42 V1 neurons during the visual-only condition. When com- paring the neuronal activity of the same cells during