Analysis of primitive linear and nonlinear stochastic systems
Texte intégral
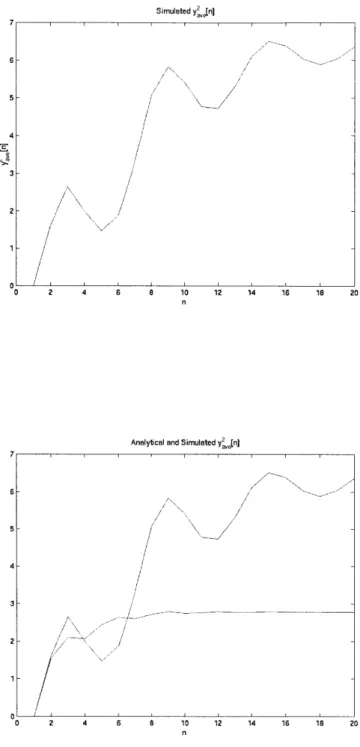
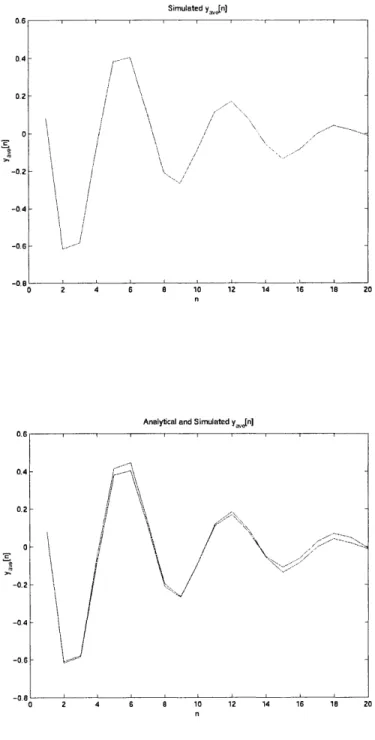
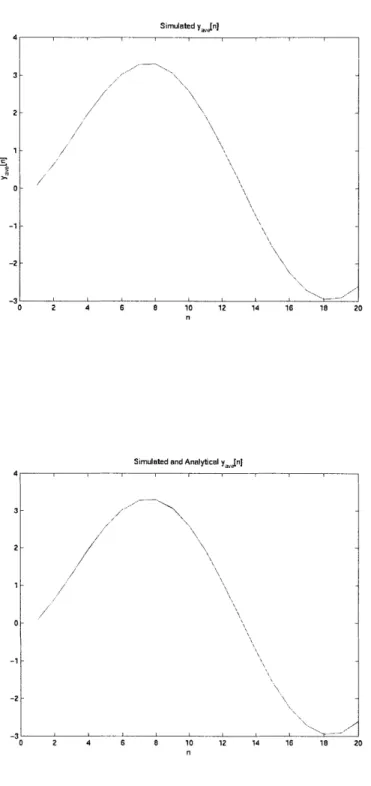
Figure
![Figure 4.2: Deterministic signal, xd2[n] = e-.15n * sin(n), used for the simulated and analytical results.](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14173785.474968/35.918.248.619.691.991/figure-deterministic-signal-sin-used-simulated-analytical-results.webp)



Documents relatifs
To protect against test release variability, the CFM Flow should keep safety stock inventory based on the variability in the distribution of the difference between the
Some recent studies have shown that metabolic profiles of corals and their symbiotic dinoflagellates change under temperature stress (Klueter et al. Therefore,
We give the cumulative distribution functions, the expected values, and the mo- ments of weighted lattice polynomials when regarded as real functions of indepen- dent random
Using the Melnikov theory, there has been performed an analysis of the limit cycles in oscillator systems described by single well Duffing equations under polynomial perturbations
In the field of state estimation and diagnosis of nonlinear systems using multiple model approach, the most of the pub- lished works considered TS models with measurable
Unknown input proportional multiple-integral observer design for linear descriptor systems: application to state and fault estimation.. Leith D.J.,
Keywords: state estimation; nonlinear systems; sensor faults; multiple models; decoupled multiple model; heterogeneous local model networks.. Nowadays, fault diagnosis systems