Sequential Monte Carlo for rare event estimation
Texte intégral
Figure
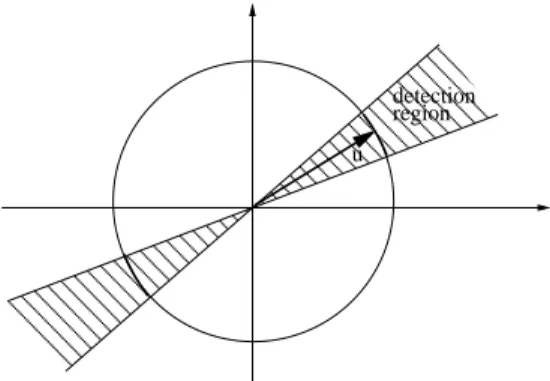
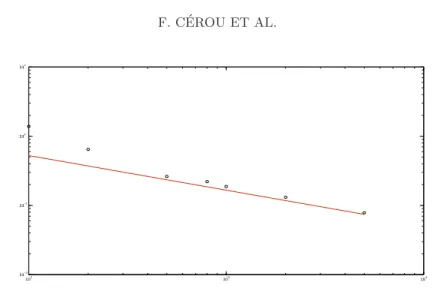


Documents relatifs
We have shown that the sampling distribution based on information projection made our IS simulation efficient to estimate the rare event probabilities which satisfy a large
We propose an adaptive rare event simulation method based on reversible shaking transformations on path space to estimate rare event statistics arising in different financial
3 Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) estimation by simulation: direct or regenerative estimator..
generating function ~g+f+!+ The elemen- tary theory of branching processes leads to precise bounds of f M and to a precise confidence interval that we can compare to the
! Overview This chapter aims at presenting the outcomes of efficient surrogate-based uncertainty propagation methods applied to an ORC turbine, namely the axial su- personic
In this paper we considered the rare event simulation problem for a switching diffusion, using a multilevel splitting method adapted to the discrete modes: the conditional
Actually we show here that computing the levels on the fly (within the same run as the one to compute the rare event probability, see algorithm 2 above, one stage procedure) we only
Keywords: rare event probabilities, extreme quantiles, cross-entropy, important sampling, splitting technique, minimum volume sets, density level sets, aerospace,