STIL balancing primary microcephaly and cancer
Texte intégral
Figure
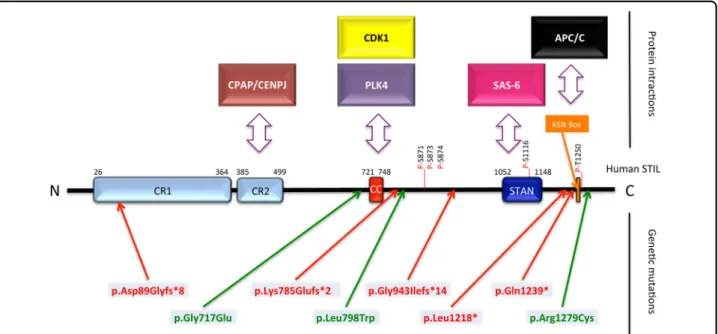
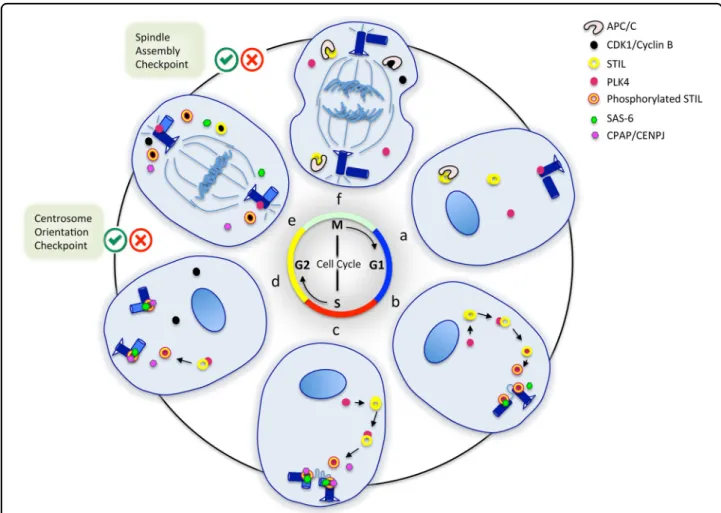
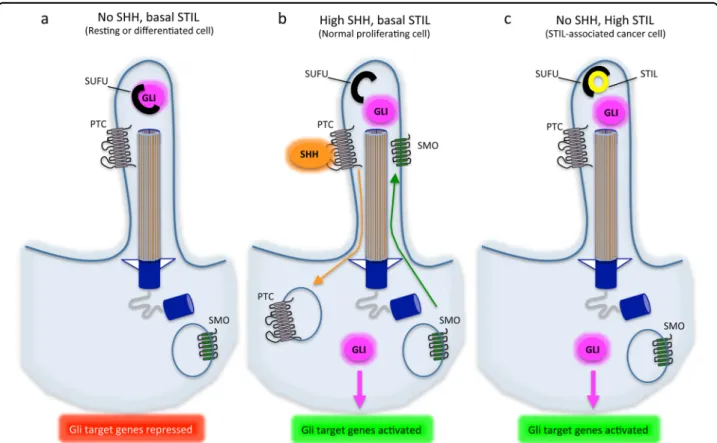

Documents relatifs
The most important result of the analyses reported above is that the speech intelligibility index obtained in the Acoustic Phonetic Decoding task is a reliable tool to
In order to investigate the impact of mast cells on sponta- neous apoptosis of neutrophils, we incubated neutrophils in the presence of conditioned medium derived from activated
Indeed, we observed in zebrafish a digenic, quadriallelic inheritance between centrosomal genes aspm and wdr62, but no genetic interaction between non-centrosomal gene casc5
40 Based on grey and secondary literature and interviews with players in the financial centre, this is undoubtedly one the most systematic attempts made thus far in the Luxembourg
To test the effect of the identified mutations on ASNS mRNA and protein levels, we generated full-length mutant cDNA constructs (p.A6E, p.F362V, and p.R550C) using PCR-mediated
Microfluorimetry experiments evaluating intracellular calcium release in response to α -latrotoxin binding showed significantly reduced cytosolic calcium release in the f œ
Aestheticism, Du Maurier (George), Iconotexts, Pater (Walter), Periodicals, Punch, Satire, Wilde (Oscar). i I am borrowing Montandon’s use of the word “iconotext”:
As soon as the level of nucleolin protein decreased (second day after transfec- tion, see Figure 1B), the number of cells increased more slowly and was almost steady compared