Nonlocal damage formulation with evolving internal length: the Eikonal nonlocal approach
Texte intégral
Figure
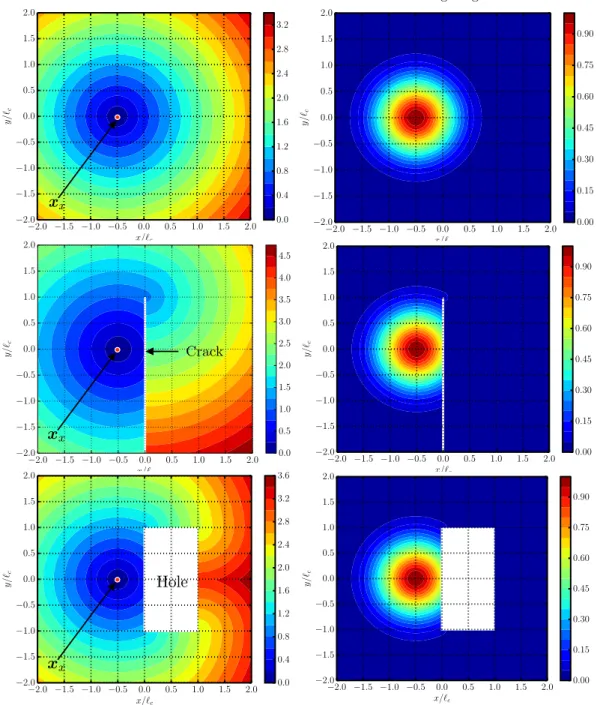

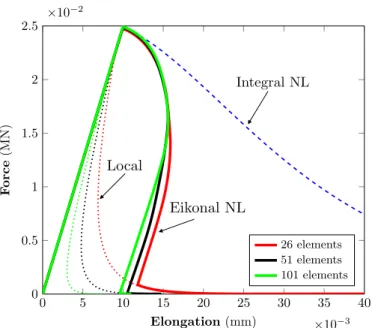

Documents relatifs
Neurologie Neuro-chirurgie Radiologie Chirurgie Cardio-vasculaire Rhumatologie Anesthésie Réanimation Anesthésie Réanimation Anatomie Biochimie-chimie Dermatologie Chirurgie
An internal time, instead of an internal length, has been introduced into the integral nonlocal theory, leading to the definition of an effective or ”dynamic” distance and to
A numerical formulation [6] for modeling damage dependent non-local interactions within mechanical computations is obtained by coupling Fast-Marching [5] algorithms
Hamilton-Jacobi equation, discontinuous Hamiltonian, viscosity so- lutions, semi– Lagrangian schemes, a-priori error
Let u be the unique uniformly continuous viscosity solution of (1.4). Minimal time function.. To prove the claim of the theorem, we will use arguments from control theory. Let x be
Nonlocal discrete ∞ - Poisson and Hamilton Jacobi equations from stochastic game to generalized distances on images, meshes, and point clouds.A. (will be inserted by
Mathematical morphology, partial difference equations (PdEs), weighted graphs, arbitrary discrete data sets, eikonal equation, nonlocal image segmentation, data clustering..
Nonlocal Hamilton-Jacobi Equations, dislocation dynamics, nonlocal front propagation, level-set approach, L 1 -estimates, geometrical properties, lower-bound gradient