Targeting the extra-cellular matrix—tumor cell crosstalk for anti-cancer therapy: emerging alternatives to integrin inhibitors
Texte intégral
Figure
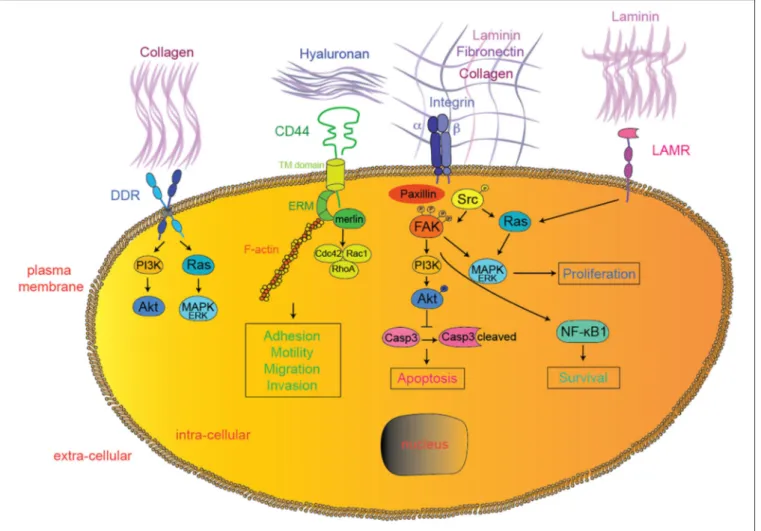

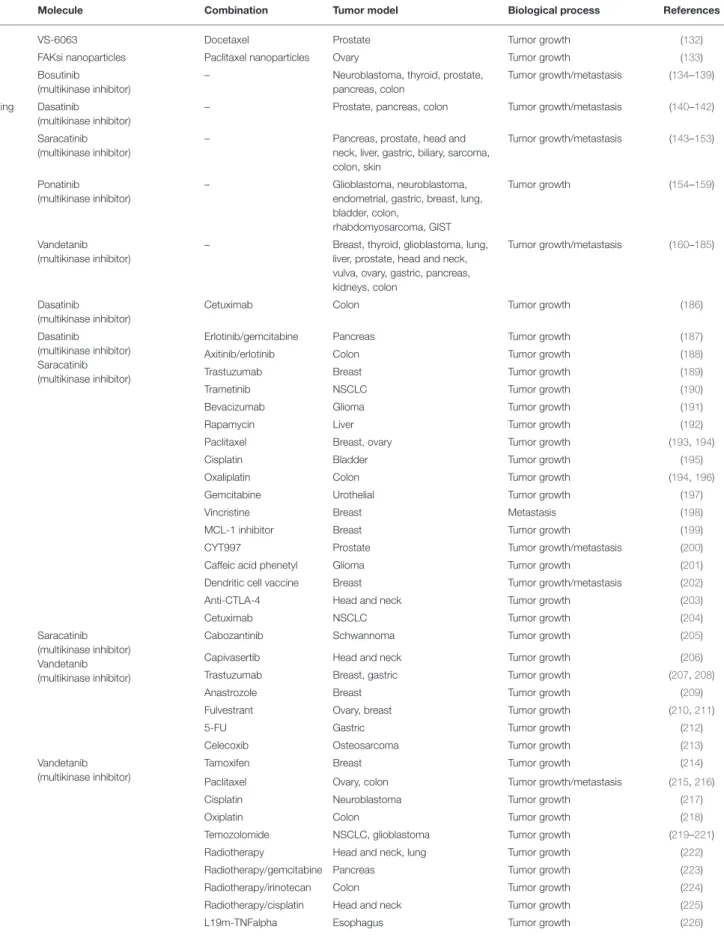
Documents relatifs
[r]
F 2 CDP acts as a sub- stoichiometric mechanism-based inhibitor (MBI) to inactivate human RNR (hRNR) (4, 10), whereas ClFTP is proposed to in- activate hRNR by binding to an
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE WEB.
It has been mentioned that one-dimensional heat flow was assumed in calculating the surface temperatures in Table iセ Measure- ments on double windows installed in the Building
Lors de la lecture d’un objet X, le client doit déterminer si la version de X stockée dans le centre de données est sûre à lire (c’est-à-dire qu’elle reflète toutes les mises
Previous cloud model studies have shown that water-soluble trace gases such as nitric acid (HNO 3 ) and ammonia (NH 3 ) can increase the cloud droplet number concentration
Expression of C/EBP TFs in Tet2 +/+ cells led to reduced and delayed mast cell differentiation ( Figures 6 B and 6F), resem- bling the phenotype observed in the absence of Tet2,
Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on clathrin- coated pit recruitment and internalization of epidermal growth factor receptor. Control of epidermal growth factor receptor