Flyweight Network Functions for Network Slicing in IoT
Texte intégral
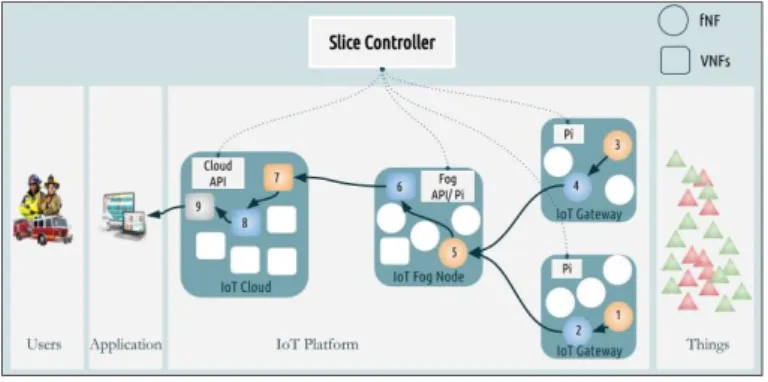
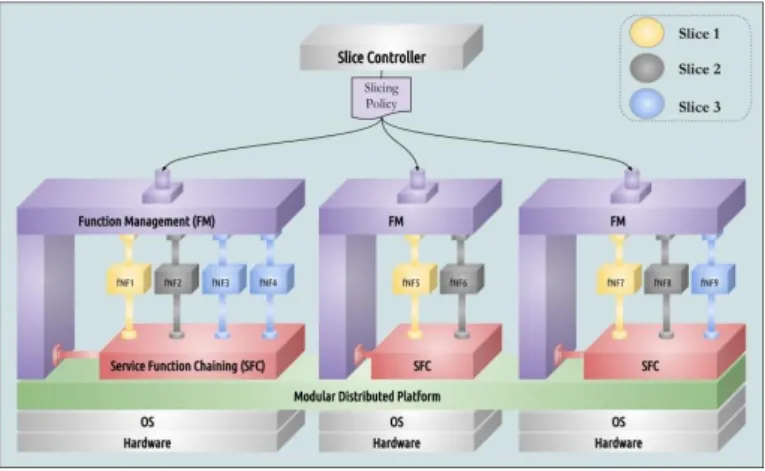
Figure
Documents relatifs
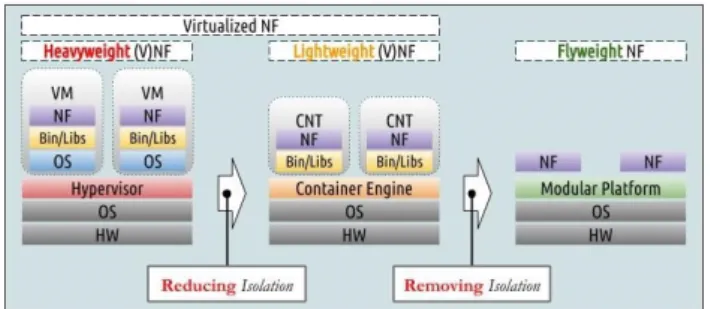
Various virtualization technologies contribute in different ways: Virtual Machine (VM) enables dynamic ways to manage physical servers; Software Defined Networking
[r]
El presente trabajo propone el dise˜ no de un nodo de convergencia ICN-IoT que integre las redes cen- tradas en la informaci´ on con el Internet de las Cosas, desde el punto de vista
In the VNF placement problem the input consists of Service Function Chains (SFC) consisting of a variable number of VNFs, whereas the substrate network, called Network Func-
ORBIT achieves good performance in terms of the link utilization and demand acceptance ratio in comparison with the optimal and offline solutions, especially when the network load
As per the ETSI MEC standard [1], a MEC platform (MEP) provides a set of services to application instances running at the mobile edge, among which is the Radio Network
The configuration option map=/boot/map defines the location of the map file, which contains the physical locations of the operating system kernels in a form that can be read by the
On the upper level, the Manager Node is where the profiling workflow is executed in a loop: (i) A workload and/or resource allocation is selected to test, (ii) instructions are given