Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging investigation of basal forebrain damage and cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease
Texte intégral
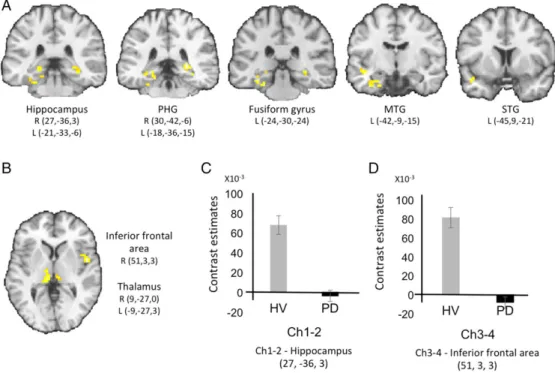
Figure


Documents relatifs
The limitations are related to the small size of our groups of patients. We focused our study on the most frequent form of frontal AD, the behavioral variant, and therefore excluded
T able 6 Mediation results: Ef fects of promotional activities on behavioural factors explaining food-related handwashing, and total indirect, direct and total ef fects of
2) Following this Permo-Carboniferous thermal surge, the temperature of the asthenosphere returned rapidly to ambient levels during the late Early Permian. With this,
As this information will inform policy for early preventative healthcare initiatives, we investigated non-periventricular frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobe white
After VRET, patients presented increased metabolism in the left frontal superior gyri and the left precentral gyrus, which showed increased metabolic connectivity with
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
(1) the auditory area caudomedial nidopallium (NCM), an auditory region that is analogous to the mammalian auditory cortex, is clearly involved in the processing/categorization
The left inferior frontal gyrus under focus: an fMRI study of the production of deixis via syntactic extraction and prosodic focus: An fMRI study of the production of deixis... THE