Atrial Signal Extraction in Atrial Fibrillation Electrocardiograms Using a Tensor Decomposition Approach
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
ﺎﺸﻗﺎﻨﻣ ﺎﺸﻗﺎﻨﻣ ﺔﺑﻮﻌﺻ ﺔﺑﻮﻌﺻ ﻟا ﻟا ّدﺎﻣ ﻲﻓ ﻞﯿﺼﺤﺘ ّدﺎﻣ ﻲﻓ ﻞﯿﺼﺤﺘ ﺔﻔﺴﻠﻔﻟا ة ﺔﻔﺴﻠﻔﻟا ة جﺎﮭﻨﻤﻟا ﻂﯿﻄﺨﺗ جﺎﮭﻨﻤﻟا ﻂﯿﻄﺨﺗ ﻢﻠﻌﺘﻤﻟاو ﻢﻠﻌﻤﻠﻟ ﻢﻠﻌﺘﻤﻟاو ﻢﻠﻌﻤﻠﻟ
Extended Data Figure 4: Association between abundant viral clusters (VCs) and host group 924. abundance and
After an evaluation on synthetic signals, the L¨owner-BTD computed by LCAGL was applied to a population of 20 patients suffering from persistent AF, whose segments are characterized
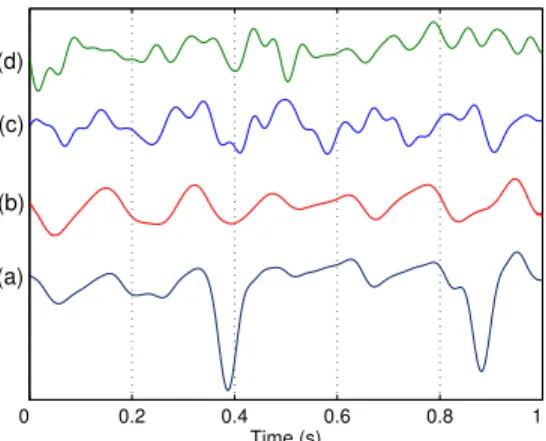
In the time domain, shown in Figure 8(a), we can see that the two last sources have the atrial signature and present a high power contribution to lead V1, while looking at the
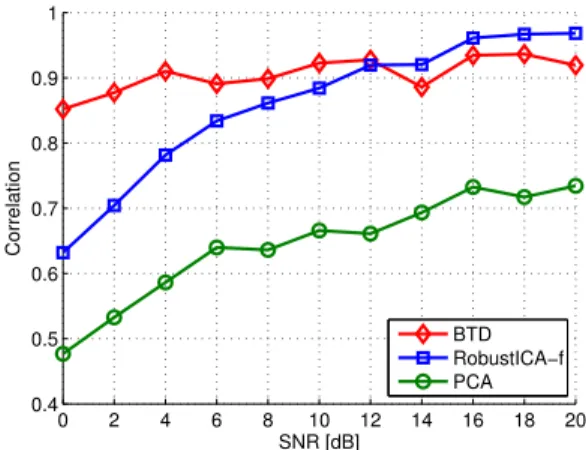
The performance of the coupled BTD for ECG source separation is now assessed in two consecutive synthetic AF segments by means of the normalized mean square error (NMSE) between
A noninvasive method to extract the AA from the cardiac signals recorded by the stan- dard 12-lead ECG is using matrix decompositions techniques to solve blind source separation
The first contribution of the present work is the analysis of BTD in time segments with varying length of an AF ECG, showing that this tensor technique presents a
Ex- perimental results using ten patients with persistent AF evaluate the proposed methods, showing their better performance in selecting the atrial source among the sources