A coupled atmosphere-ocean model of thermohaline circulation, including wind-driven gyre circulation with an analytical solution
Texte intégral
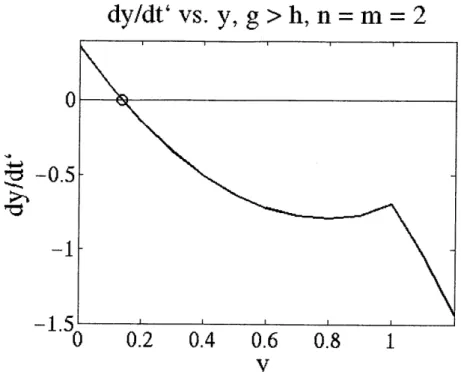
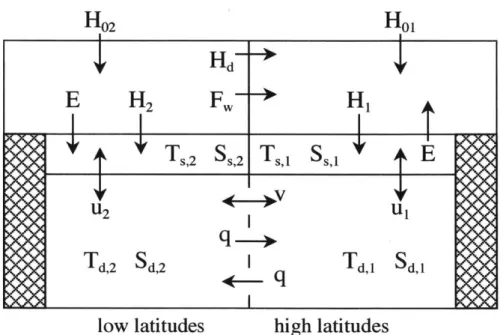
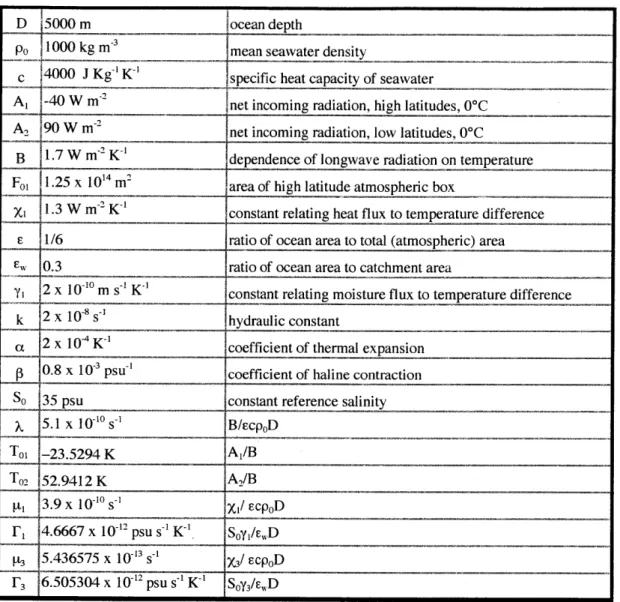
Figure


Documents relatifs
However the Stokes drift of a spe trum of wind waves is strongly surfa e trapped so that, in the presen e of a strong verti al mixing, δ s ≪ δe and the mean ow driven by
This means that a strong initial THC weakens more under global warming as long as the temperature dif- ference between ocean and atmosphere averaged over the North Atlantic area
Seasonal forecast of tropical climate with coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation models: on the respective role of the atmosphere and the ocean components in the drift of
The structural information obtained from the MS methodologies mentioned above are often coupled to computational approaches in order to unravel the atomistic details of
These methods are asymptotically equivalent and require the same assumption that the data are missing at random (MAR), i.e., the missing data mechanism depends on observed values
This suggests either that climate change is not the main driver for observed soil carbon losses or that the ORCHIDEE model even with priming or N effects on de- composition lacks
L'ouvrage s'achève sur un trop bref chapitre d'une dizaine de pages consacré à "l'essor de la Géologie", dans lequel l'auteur tente de passer rapidement en revue les