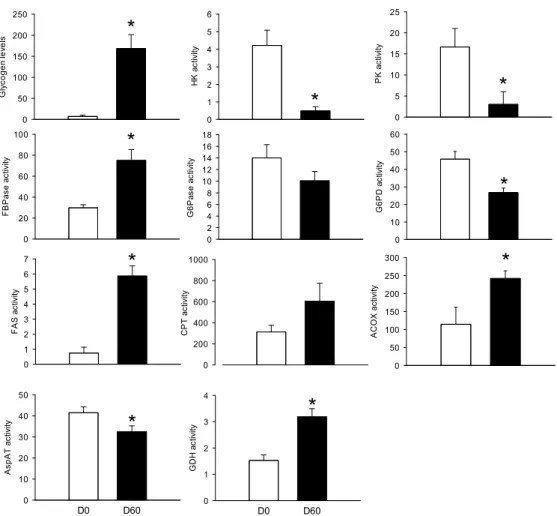
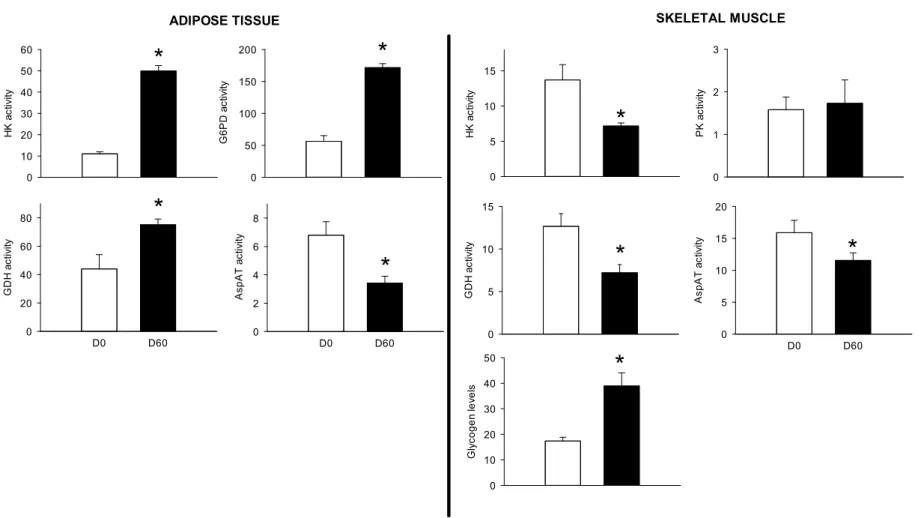
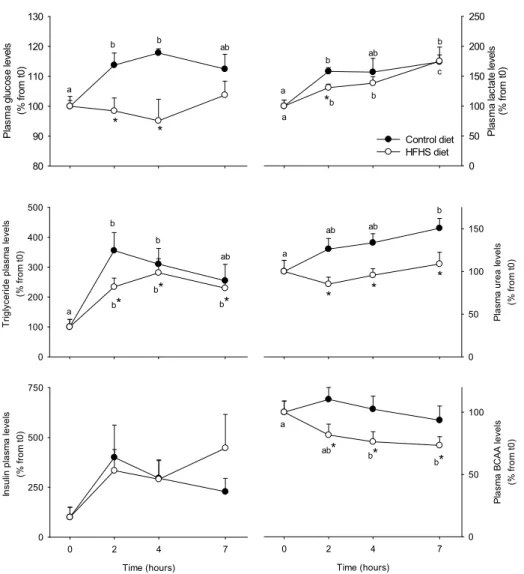
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Metabolism Acutely Adapted to Postprandial Transition and Mainly Reflected Metabolic Adipose Tissue Adaptations to a High-Fat Diet in Minipigs
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
TABLE 5: Growth parameters and Nhe production determined from uncontrolled batch cultures of ldhA, pfo, ldhB and ldhC mutants and their parent strain F4430/73 (wt).
Assessment of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity using CareStart G6PD rapid diagnostic test and associated genetic variants in Plasmodium vivax malaria endemic setting
Their results revealed that neither C149S nor C149S/C281S mutants aggregated, proposing that the active site cysteine of GAPDH plays an essential role in amyloid binding,
Molecular analysis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogen- ase deficiency in this study conducted in Jeddah revealed a higher prevalence of G6PD Mediterranean (89.1%) and Aures
To assess inter- and intra-laboratory variability in G6PD spectrophotometry, data from the measurement of manufacturer-provided quality control samples were used to quantify
Since in two sites (Vietnam and Laos) only phenotypically deficient and intermediate samples were genotyped (and the propor- tion of heterozygous women with normal G6PD pheno-
Furthermore, SAR analysis of EA analogues supported by docking models provides clues towards the determinants for the selective inhibition of the pathogen enzyme by steroids: (i)
We coupled these results with compu- tational biology analyses along with subcellular localization experiments to propose two mitochondrial kinase enzymes (T. gondii PDK [TgPDK] and