Liquid crystal ionic self-assembly and anion-selective photoluminescence in discotic azatriphenylenes
Texte intégral
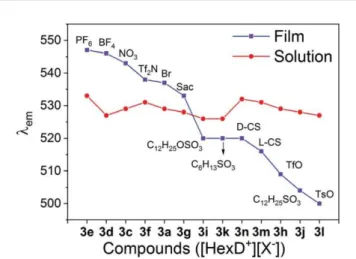
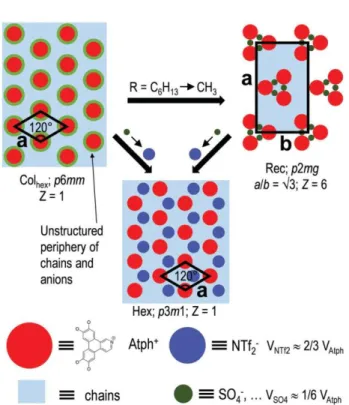
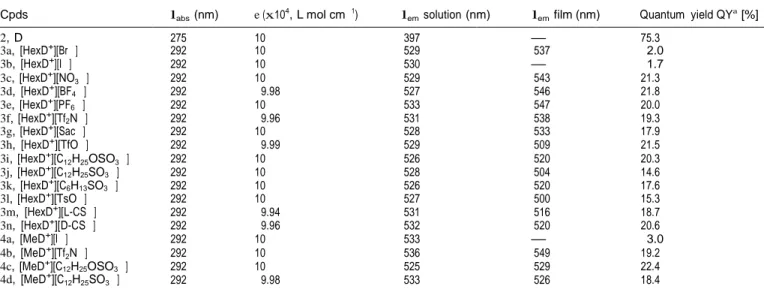
Figure


Documents relatifs
with the smectic layers along the rubbing direction at high polymer concentrations and, typical of low molecular weight liquid crystals, normal to the rubbing direction
It yields a measurement of the capillary length do (proportional to 03B3/L ; 03B3 is the surface tension and L the latent heat) and of the diffusion coefficients of
While the left spectrum features a normal SmA*-SmC a * transition, distinguished by a SmA* soft mode with an absorption maximum just above the transition and a fairly sharp drop
Pitch measurements and dielectric spectroscopy reveal that there is a strong hysterisis in the phase sequence on cooling and heating and that the phase temperature intervals depend
are that experimentally, we find that K33/Kii is substantially reduced for a bent dimer and that the elasticities of the odd dimer are considerably smaller than for the even dimer,
monomers, we obtain a complete statistical description of the nematic phase with expressions for order parameter, mean-field potential, phase transition parameters and Frank
A cluster model of ordering, mcluding short-range dipolar orientational order, quantified by a parameter T, was used to attempt a more reasonable prediction of dipole correlation
X.U. Post-hydrogenation significantly re- duces the gap state density of LPCVD a-Si. Phosphorus and boron ion-implantation sho~v that .;PCVD a-Si has a higher doping