An Asymptotic-Preserving all-speed scheme for the Euler and Navier-Stokes equations
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
preserving all Mach number scheme for the Euler equations of gas dynamics, SIAM J. Sharp, A conservative Eulerian formulation of the equations for
While almost all the schemes mentioned before are based on very similar ideas, the approach proposed in [23] has been shown to be very general, since it applies to kinetic equations
The standard discretization is not able to reproduce the electron flux as the standard numerical scheme is not able to reproduce the limit when the electron inertia is very small,
Our study is concerned with the analysis of the low Mach number limit for classical solutions of the full Navier Stokes equations 1.3 in the nonisentropic general case and for
Uniform spectral convergence of the stochastic Galerkin method for the linear transport equations with random inputs in diffusive regime and a micro-macro decomposition based
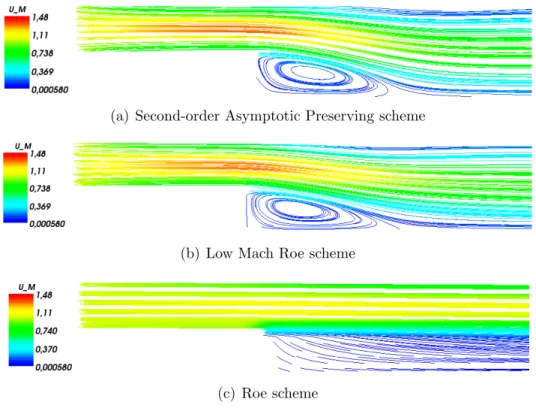
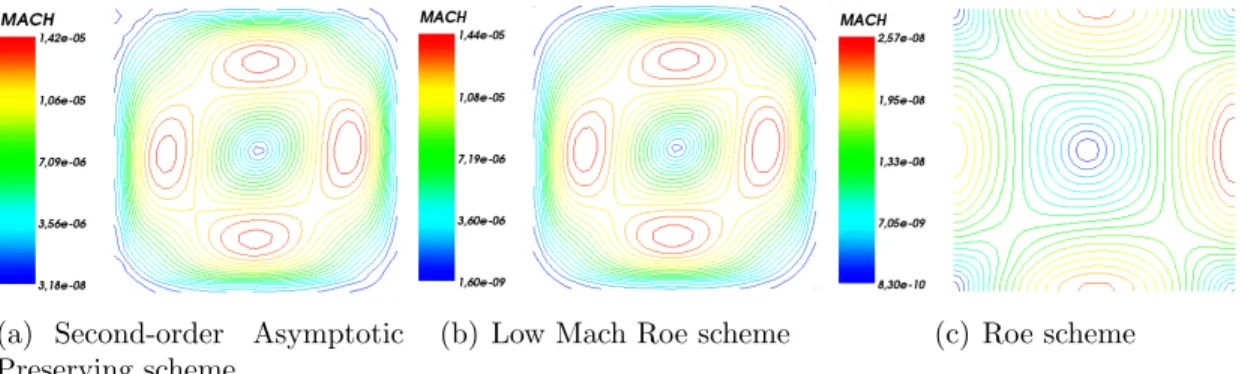
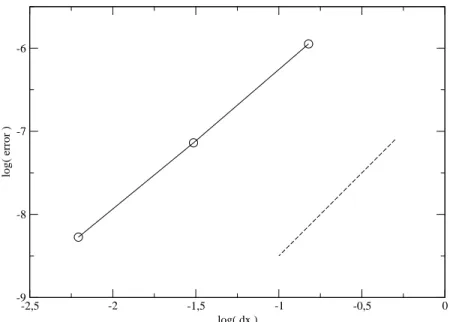
In all the numerical simulations conducted we employ the second order scheme that is described in section 3.4, which is based on Strang splitting for the Vlasov equation and the
Figure 12: Relative difference between the computed solution and the exact drift-fluid limit of the resolved AP scheme at time t = 0.1 for unprepared initial and boundary conditions ε
The AP property of the new scheme is achieved by splitting the relaxation system into a non-stiff nonlinear, compressible hyperbolic Navier–Stokes like system and a system that can