Search for squark production in events with jets, hadronically decaying tau leptons and missing transverse energy at sqrt(s)=1.96 TeV
Texte intégral
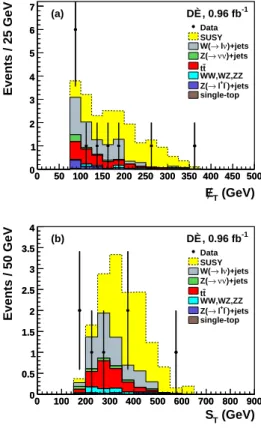
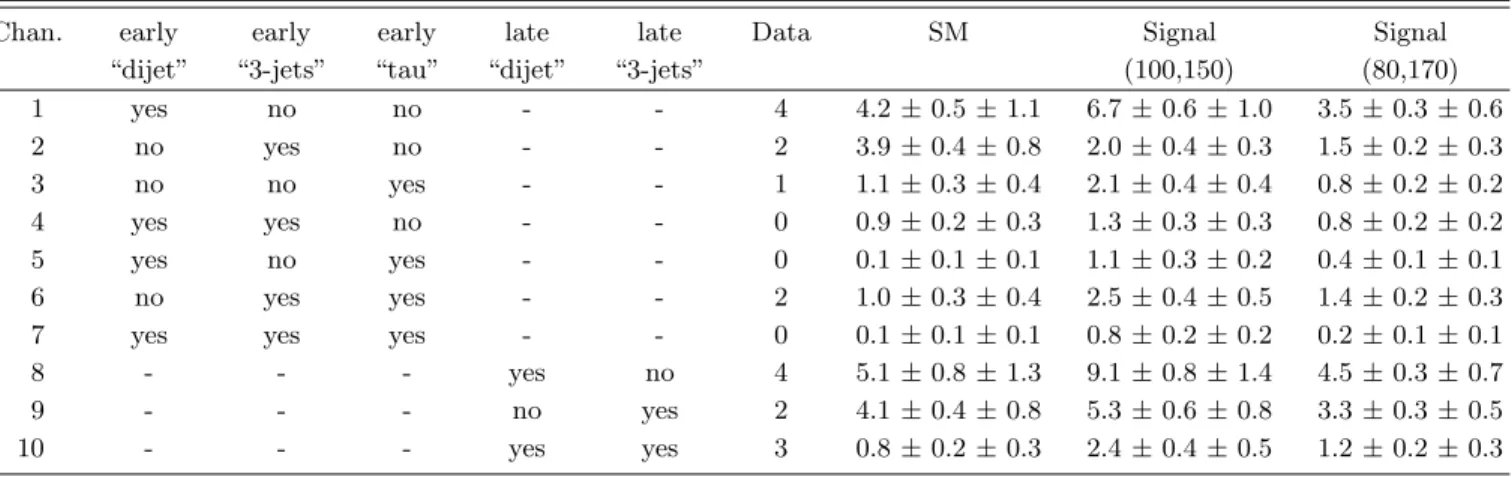
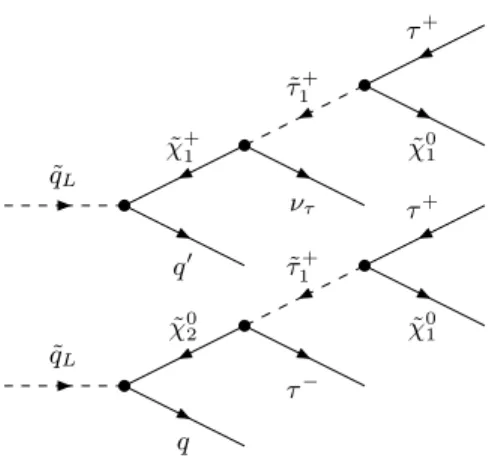
Figure



Documents relatifs
Table 7: Systematic uncertainties in units of 10 −2 from the following sources: momentum measurement from tracking in the magnetic field (TPC), energy measurement in the ECAL (ECAL),
of Cells Theorem in that we will increase the size of all the messages passed around inside the lexical analyzer to include what would have been the contents
It is shown that implementation of a projection algorithm with standard adaptive control of a scalar plant ensures global boundedness of the overall adaptive system for a class
National Research Nuclear University ’Moscow Engineering Physics Insti- tute’ (MEPhI), Moscow, Russia.. Lebedev Physical Institute,
As part of each analysis, the t¯ t and W +jets backgrounds are estimated using dedicated control regions (CRs), making the analysis more robust against potential mis-modelling
To this end, meteoric 10 Be, 137 Cs and 210 Pbxs concentrations were measured in six soil profiles representative of 5 soil types contrasted in terms of physico-chemical
The asymmetric void distribution can be rationalized based on the phase with the lower surface energy and wetting of interfaces with heterogeneous formation energies.. These