Lipoprotein Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Texte intégral
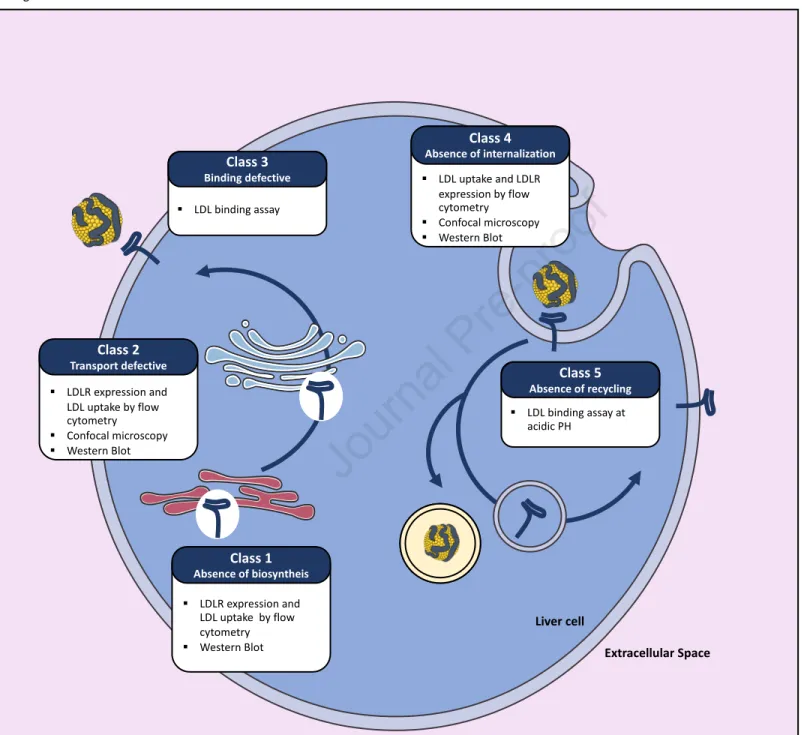
Figure
Documents relatifs
tinine serait plus sensible que celle du DFG pour détec- ter la NPC, mais la corrélation clinique de cette variation d’incidence reste à évaluer. En effet, près de la moitié
iens, due to technical restrictions and the amplifications of this gene in the Wolbachia harboured by this species, we investigated here the putative link between CI mod
Thus, the localization of the B4GALNT2 gene within the minimal locus, the presence of the SNP g.36938224T.A on OAR11, localized in the intron 7 of this gene as the possible
Plasma apolipoprotein E (apo E) and apolipoprotein(a) levels were measured by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry in plasma samples isolated from 444 nontreated patients
Although no sign of cell apoptotis was observed at the time of implantation of the cell constructs, the number of TUNEL positive cells increased at day 6 post-implantation, peaked
The novel LDLR gene mutation identified in this family, 756del7, induces a frameshift with creation of a stop codon at position 241 and it would cause a class 1 LDL receptor
Our results thus confirm the value of salvage therapy based on foscarnet plus AZT, 4,5 in patients selected for their overall resistance profile and not for the number of TAMs, and
Results: We identified three novel mutations (C25X, IVS3+5G>T, D558A) and two mutations previously described (D151N, A480E) in the LDLR gene.. The R3500Q and R3531C mutations