Bee Venom and Its Component Apamin as Neuroprotective Agents in a Parkinson Disease Mouse Model
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
Current political developments in Nepal, India, Pakistan and China Ind the implications of these developments for resea rch carried out by European scholars.. The
The theory of spaces with negative curvature began with Hadamard's famous paper [9]. This condition has a meaning in any metric space in which the geodesic
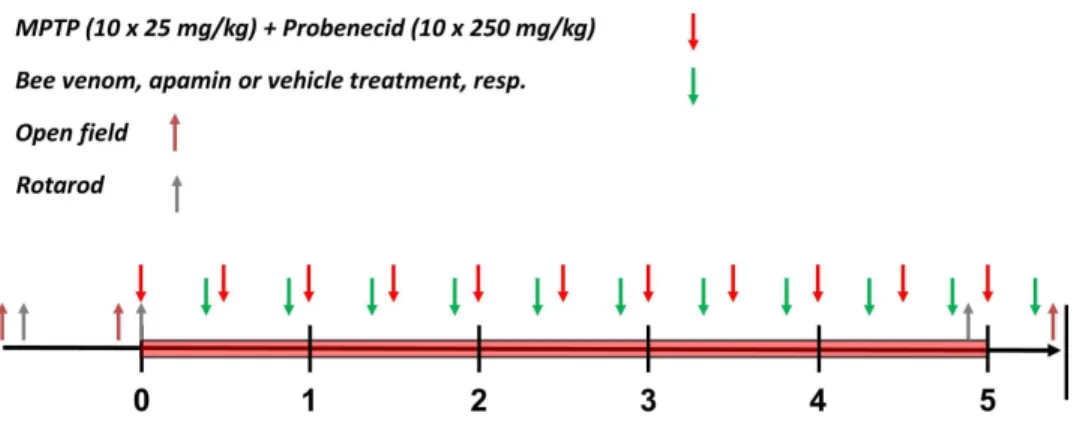
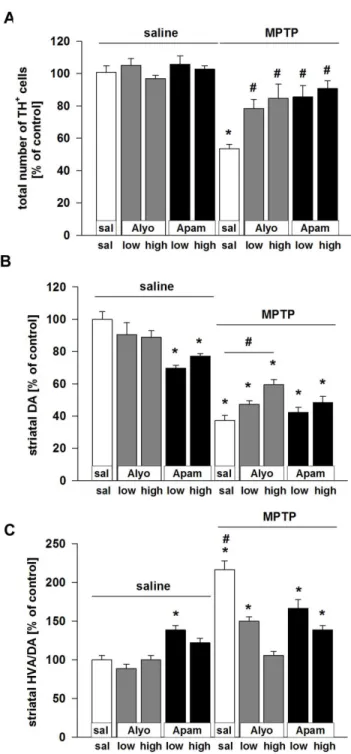
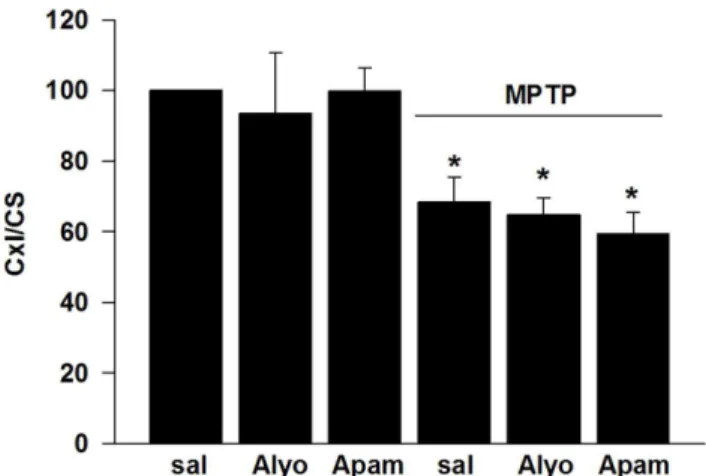
Bee venom restores functional balance in the basal ganglia subcircuits The site of action of BV in the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical circuit is an important issue. To
In summary, we have shown that microglial DAP12 and CD11b contribute partially to microglia-associated DN cell death in vitro and that DAP12 is reactivated during PD-like
BV is produced by female worker bees and is known to contain many active components including: (i) peptides like melittin, apamin, mast cell degranulating (MCD) peptide, and adolapin,
The microsporidian Nosema apis infects the epithelial cells in the ventricu- lus of the honey bee, Apis mellifera.. The spore produced by the parasite is
Index Terms—Business to worker, multiagent system, multiagent architecture, generic service component, field trial, virtual
2 Until a refrigerator-stable vaccine becomes available, however, varicella vac- cine will not be incorporated into the recommend- ed immunization schedule in Canada, as most