Immune responses during COVID-19 infection
Texte intégral
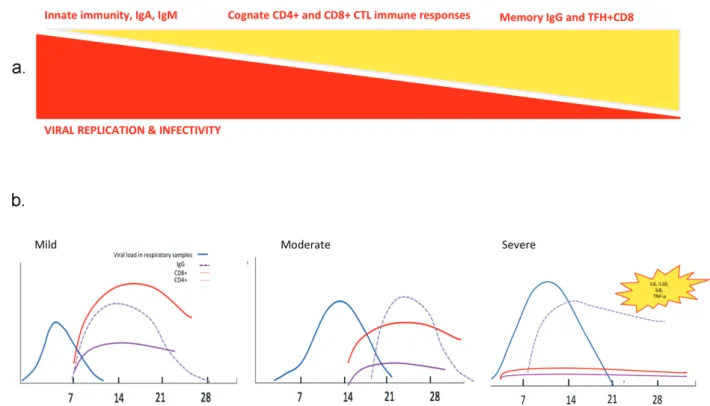
Figure


Documents relatifs
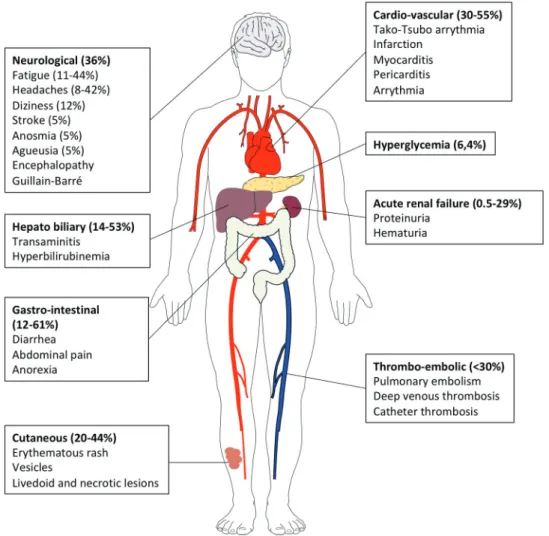
Recently, however, reports from Europe and North America have described clusters of children and adolescents requiring admission to intensive care units with a multisystem
The systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is the body response to injury or insult, infectious or non-infectious condition characterized by a hyperinflammatory state.. SIRS
Based upon these previous data, the aim of the present study was to evaluate whether serum soluble TWEAK could be a reliable biomarker of neuroinflammation in MS patients. We
expression, we FACS purified eYFP + and eYFP – CD4 T cells from draining lymph node and spinal cord of MOG-CFA immunized mice and stimulated the cells in the presence of..
To understand the underlying molecular differences in host response, primary chicken and duck lung cells, infected with two HPAI H5N1 viruses and a low pathogenicity avian
MPs, microparticles; EMPs, endothelial cells derived microparticles; PMPs, platelets derived microparticles; HD, healthy donors; SSc, systemic sclerosis; MTX, methotrexate;
Les deux dernières sont généralement basées sur une réaction de dérivatisation de l'histamine avec l'orthophthalaldéhyde (OPA). L'inconvénient majeur du dérivé
The HLA-B, HLA-C and KIR genetic profiles were deter- mined from 162 individuals divided into four groups as follows: Group 1 - individuals infected with HIV-1 and