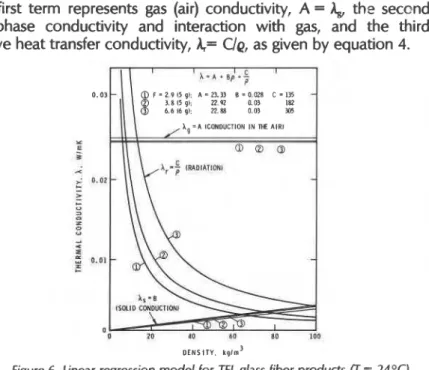
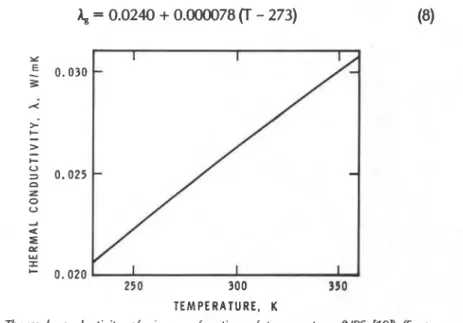
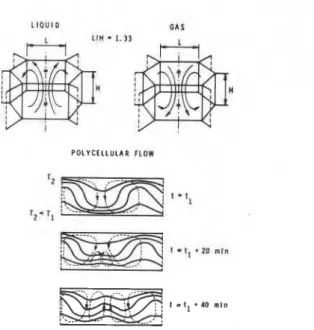
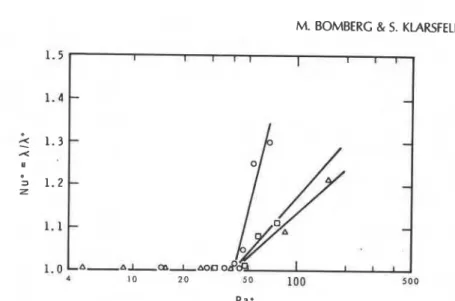
Semi-empirical model of heat transfer in dry mineral fiber insulations
Texte intégral
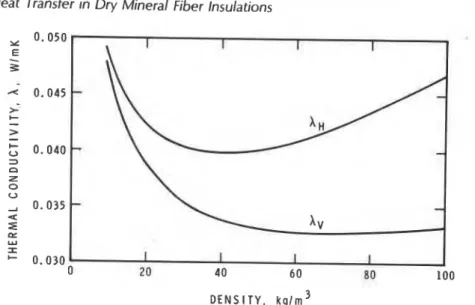
Figure



Documents relatifs
Et c'est peut- être cela que les Fribourgeois, contre vents et marées - parce que tout ne fut pas toujours facile pour eux - ont conservé leur propre identité et maintenu le
On the other hand, a slow reaction wave allows the reacted region to cool on the same time scale as the wave propagation, creating a temperature gradient in the opposite
In order to avoid direct electrolysis, the concentration of mediator and the applied current density was increased so that the rate of production of the anion radical interme- diate
It is important to build reliable and efficient numerical models to represent the physical model of heat and mass transfer in porous building material.. The reliability of a
Test Case 1 concerns the estimation of an optimal time-dependent heat flux q(t) that makes possible the simultaneous estimation of all Luikov’s parameters of cer- amics from a
In order that the predicted fiber orientation captures both the correct skin–shell–core structure and a global radial evolution along the flow path, in the discrepancy function,
Abstract : We proposed a study digital, by finite difference, heat transfer in a multilayer wall (three layers) subjected to radiation condition on the inner side and taking
Given that the macroscopic equation recovered by this model is only valid in the limit of incompressible flows with constant heat capacities, one would, for example,
![Figure 5. Structural parameters in hnkvall's model [3] shown for one unit of volume (From Bankvall[3l)](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14319204.496722/9.606.179.504.93.333/figure-structural-parameters-hnkvall-model-shown-volume-bankvall.webp)