Attentional bias modification with a new paradigm: The effect of the Detection Engagement and Savoring Positivity (DESP) task on eye-tracking of attention
Texte intégral
Figure



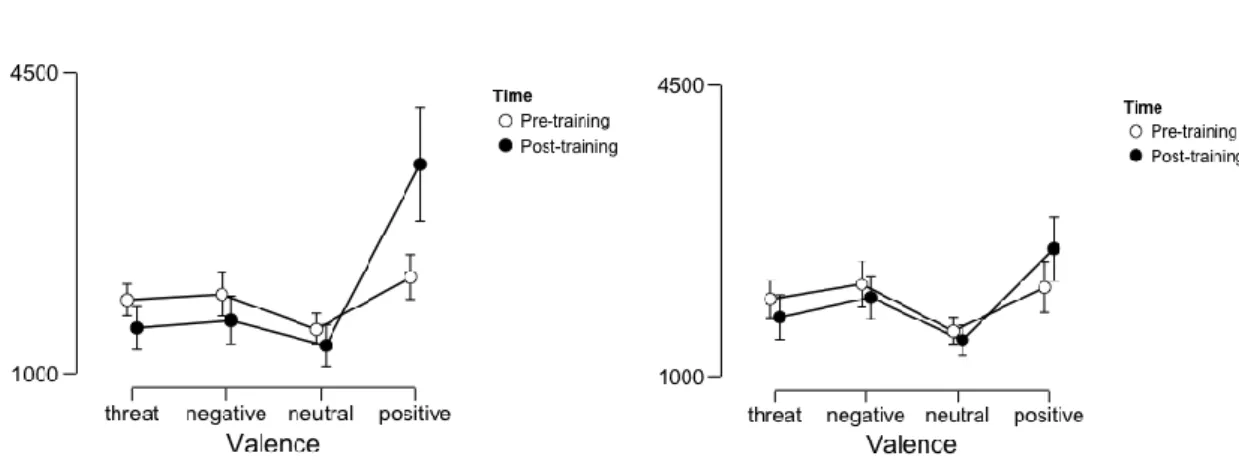
Documents relatifs
To summarize this brief history, even if eye gaze tracking systems exist since a long time, the tracking and measure of eye behaviour and gaze di- rection was until recently a
Our results differed from prevailing developmental models (e.g., Denney 1984 model) in the sense that there were no differences in anticipatory responding (i.e., conditioned
At all assessment sessions (baseline, post-training, and follow-up) participants completed the measure of pain symptoms (primary outcome), followed by the measures
McGowan and colleagues, who were the first to investigate the effects of a single ABM training session on pain, found that training attention away from pain words changed the
The presence of an attentional bias towards alcohol is indexed by faster reaction times when the probe appears at the same location than the alcoholrelated stimulus as illustrated
After considering future research directions of Miranda et al., and thoroughly reviewing all the related literature on social media dimensions and political opinion, we found
We used Equations 15 and 16 to calculate the difference between the reference and focal factor-analytic TCCs and obtained results in harmony with our item-level analysis: Number
Theories of the diffusion of ideas in social psychology converge on the assumption that shared beliefs (e.g., social representations, rumours and legends) propagate because they
