Disentangling climatic and anthropogenic controls on global terrestrial evapotranspiration trends
Texte intégral
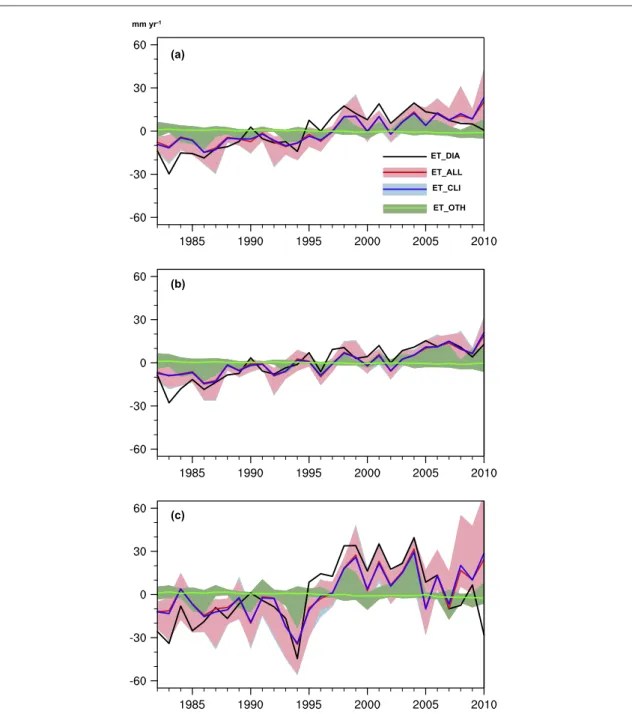
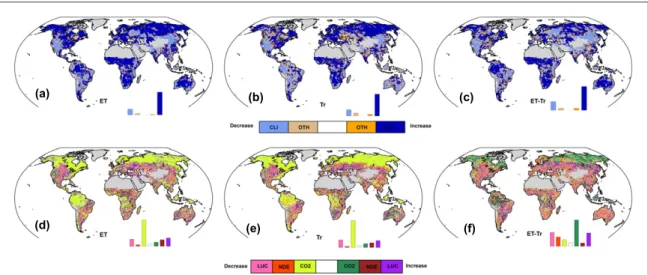
Figure


Documents relatifs
Large-scale land acquisitions as aggravator Drivers Food production Biofuels Industrial production Forest/fibre production Ecosystemic Services/Turisme Speculation Triggers. Food
Mobilisation by the European Union of the existing mechanisms makes it easy to define a common vision of the global challenges faced by agricultural research, and to discuss within
The objectives of this study are (1) to document a new LUC module, including sub-grid vegetation cohorts, forest harvest, and gross LUC in the ORCHIDEE model, that can be run with
Relative positions of median ecosystem in the ecosystem functioning space: Ecosystem types (colours, labels) in each climatic zone (shapes) according to the
In autumn, the GKSS and CNRM models simulate a decrease in rainfall over the 2021-2050 period (Fig. 6) which is more significant in Algiers (GKSS), Oran (GKSS and CNRM) and
(2010), price-induced effects on land-use can be summarized as follows: (i) reallocation of production among countries (through international trade) and agricultural
Large-scale land acquisitions as aggravator Drivers Food production Biofuels Industrial production Forest/fibre production Ecosystemic Services/Turisme Speculation Triggers. Food
Facilitators -Land governance -Democratic governance -Economic governance and market regulations -Crisis of family farming (the perception thereof) A GOVERNANCE PROBLEM
