HyLAR: Hybrid Location-Agnostic Reasoning
Texte intégral
Figure
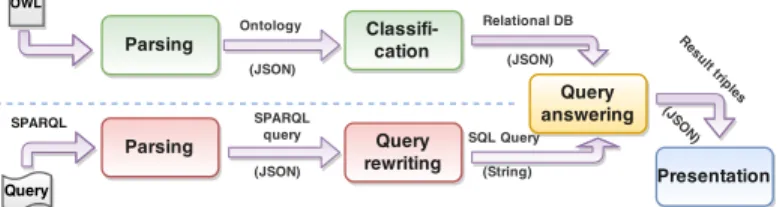

Documents relatifs
In this paper, we describe the Knowledge Organisation Sys- tem Implicit Mapping (KOSIMap) framework, which differs from exist- ing ontology mapping approaches by using description
Our example illustrates how the algorithm using functional knowledge about object and agent interactions produces two valid placements for a printer given a
By using new features provided in Android API Level 21, it is now possible to access battery information such as voltage, current flows in order to calculate the accurate
They are: establishing a baseline, the effect of the presence of the DOLCE foundational ontology to which DMOP is linked, the effect of using inverse object properties versus OWL 2
In this paper we have studied which published indicators of reasoning perfor- mance for ontologies that carry over to Ontology Design Patterns, and how those indicators are expressed
We consider four scenarios, representing all possible steps of the reasoning process: the scenario (0) for loading client scripts; (1) for loading a raw ontology; (2) for
The proposed activity ODP also distinguish two types of activities, namely Fixed Activity and Flexible Activity, as defined in the time geography literature [8,4].. These two types
Basically the algorithm is divided into two separate steps to handle temporal and legal reasoning: (1) Determine which rules are applicable to a case at a certain point in time