Bioassay-guided isolation and UHPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS quantification of potential anti-inflammatory phenolic compounds from flowers of <i>Inula montana</i> L.
Texte intégral
Figure

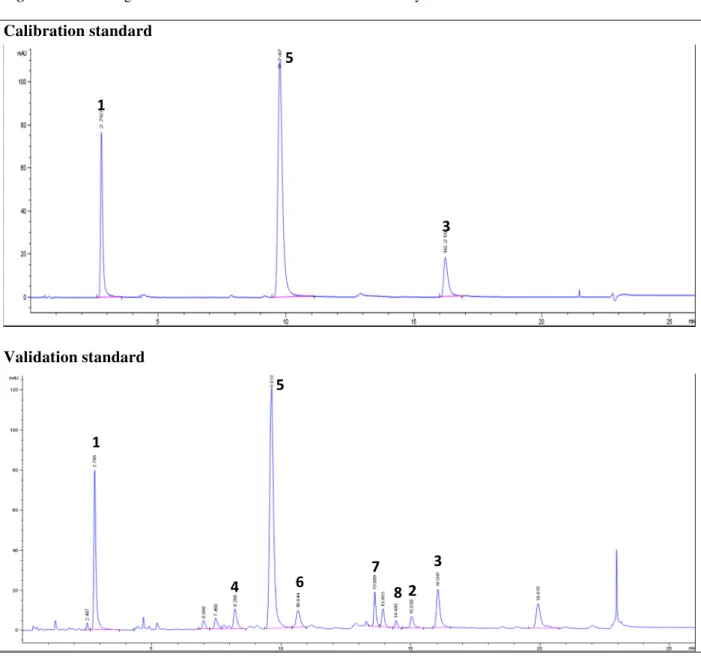
![Table 2 Spectroscopic data of compounds of the extract L2E analyzed by UHPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS Cmpd n o R t (min) λ max (nm) [M+H] + (m/z) MS/MS (m/z) Identification 1 2.8 240-326 355 185-215 Chlorogenic acid 4 8.2 242-328 517 - 3,5-O-Dic](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13696905.432948/14.892.93.796.116.540/table-spectroscopic-compounds-extract-analyzed-uhplc-identification-chlorogenic.webp)

Documents relatifs
Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) method has recently been employed to characterise the alkaloids of Stephania tetrandra S.Moore (Sim et al.,
Determination and Comparison of Phospholipid Profiles in Seven Kinds of Egg Types Using UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS... 2
of submitted results for Case 1 report a total duration estimate which is different by less than 1% compared to the true duration. Some participants arrived at the exact
The identification of Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for tomato aroma volatiles identified in experimental populations involving different wild tomato species have delivered
Digital records with a diagnosis of jaundice were classi- fied into three categories: i) clinical jaundice without la- boratory confirmation (excluded from the analysis), ii)
Le « sapeur » est un futur aventurier dans le sens où c’est seulement à partir du moment où il a pu accomplir un retour glorieux au pays après un séjour fructueux dans
6: Direct comparisons between experiments (plain curve) and theory on the energy decay in the granular medium. Black squares: theoretical predictions on the basis of a constant
Indeed, we found that HACE1(S385E) is catalytically active on Rac1 in vitro (Fig. 4f ), though it displays low activity in cells (Fig. 4b ), suggesting the combined involvement of