Robust supervised classification and feature selection using a primal-dual method
Texte intégral
Figure

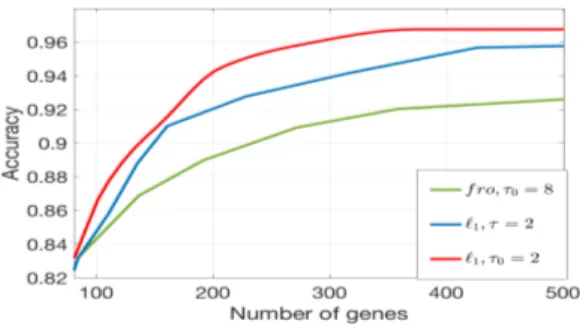
Documents relatifs
This work leverages on a new approach, based on the construction of tailored spectral filters for the EFIE components which allow the block renormalization of the EFIE
At this point we remark that the primal-dual active set strategy has no straight- forward infinite dimensional analogue for state constrained optimal control problems and
We propose a new first-order splitting algorithm for solving jointly the pri- mal and dual formulations of large-scale convex minimization problems in- volving the sum of a
The worst-case complexity bounds for the problem (1) with the exact and stochastic first order oracle are available for the case of strongly convex objective (see, e.g... [18, 1]
An algorithm for efficient solution of control constrained optimal control problems is proposed and analyzed.. It is based on an active set strategy involving primal as well as
A few questions remain open for the future: A very practical one is whether one can use the idea of nested algorithms to (heuristically) speed up the con- vergence of real life
We compare Algorithm 1 with two competitors: k·k 1 -composite stochastic subgradient method (SSM) for the primal problem (1), in which one uniformly sam- ples one training example at
r´ eduit le couplage d’un facteur 10), on n’observe plus nettement sur la Fig. IV.13 .a, une diminution d’intensit´ e pour une fr´ equence de modulation proche de f m.