A Grid-enabled Branch and Bound Algorithm for Solving Challenging Combinatorial Optimization Problems
Texte intégral
Figure
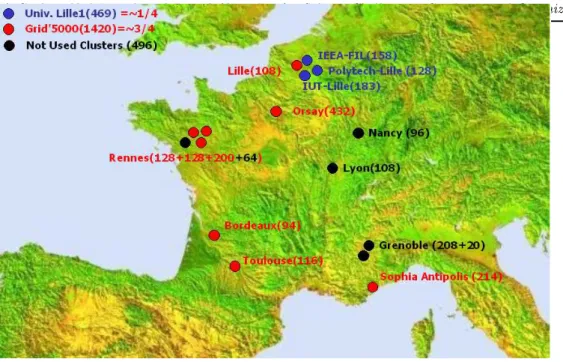
Documents relatifs
The goal of the present study was twofold: testing with fMRI whether the real color sensitive areas of synesthetes were involved in their experience of synesthetic colors
Dans la seconde phase du raisonne- ment, le juge se penche uniquement sur les conditions posées par l’article 1322, alinéa 2, du Code civil (en matière de signature
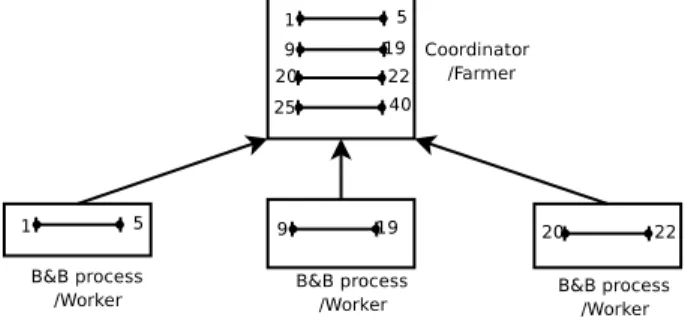
The web application (Figure 1) allows users to upload corpora, to index docu- ments with specific web services in order to mark different kinds of information (spatial
Results: A NimbleGen microarray containing 39,179 UniGenes was used to study the kinetics of gene expression during wheat grain development from the early stages of cell division to
Les restaurations des lésions cervicales non carieuses réalisées avec l’adhésif Optibond All- In-One associé au composite Herculite ® XRV Ultra avec ou sans mordançage
Machine learning (ML) techniques are also good approaches for solving COPs [2]. In this regard, the hybridization of ML techniques with MHs is an emerging research field that
Table 4 reports the size of the critical tree for five branching rules (two static rules Forward, Alternate, and three dynamic strategies MaxSum, MinMin and MinBranch) and two
This rounding heuristic consists in fixing to 1 all binary variables greater or equal to 0.5 (the k great- est ones if there are more than k for the ROPF problem with