Drug/protein interactions studied by time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy
Texte intégral
Figure
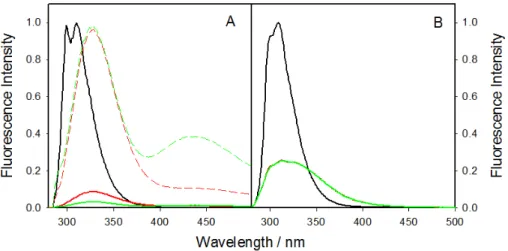
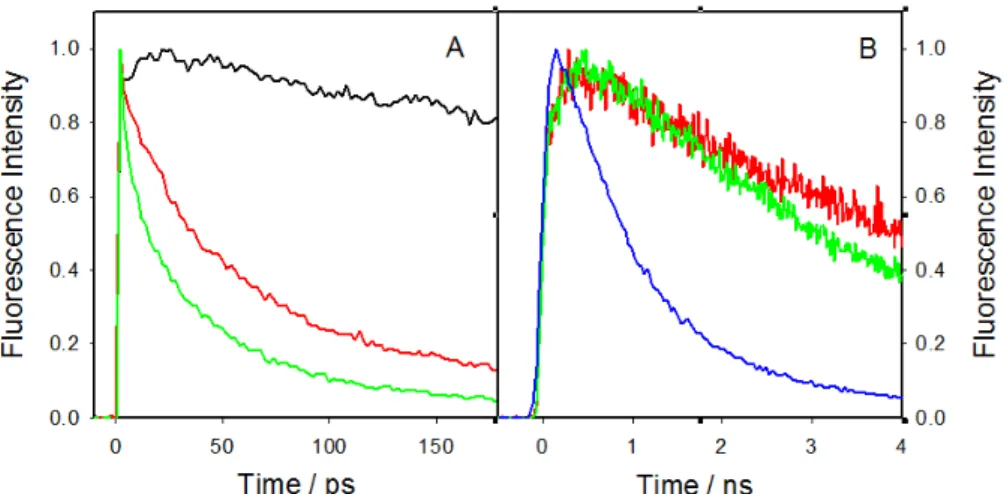
Documents relatifs
The significantly lower amount of NCp7 and lower FRET efficiency in the nucleoplasm, to- gether with the lower sensitivity of the FRET efficiency upon RNase treatment further
The actual termination efficiency cannot be determined as the control 113514 has a majority of cells that produce no significant fluorescence, and cannot be used to
The first instrument (called LEDIF) employs a novel flowcell, 6 UV LEDs as excitation sources, a wideband lamp, and a spectrometer to measure steady state chemical
First, we extend the concept of SPARQL graph pattern defined over a crisp RDF data model, to the concept of fuzzy graph patterns that allows: (1) to query a fuzzy RDF data model,
Equilibrium constants in aqueous lanthanide and actinide chemistry from time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy: The role of ground and excited state reactions.. By Isabelle Billard
The current methods are based on intraoperative surgical fluorescence microscopy [4] or optical fiber systems that allow a local emission spectrum measurement [5],[6] or
Acyclic queries can be recognized in linear time (see [TY84]) and various efficient algo- rithms have been developed to evaluate them (see for instance [Yan81], [PY99], [GP01]