Parametric inference for mixed models defined by stochastic differential equations
Texte intégral
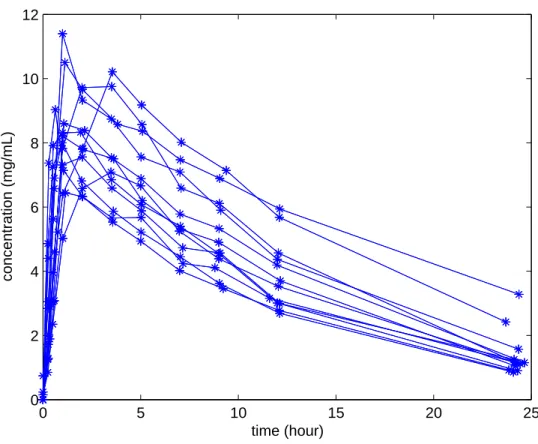
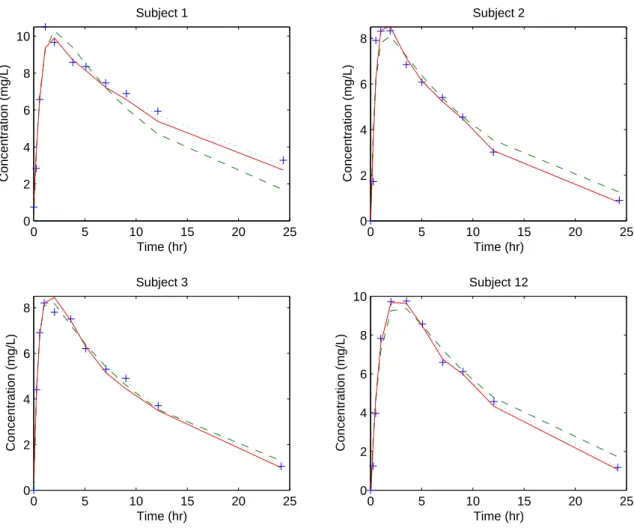
Figure
Documents relatifs
Note that generating random samples from p i (ψ i |y i ) is useful for several tasks to avoid approximation of the model, such as linearisation or Laplace method. Such tasks include
Since the individual parameters inside the NLMEM are not observed, we propose to combine the EM al- gorithm usually used for mixtures models when the mixture structure concerns
Keywords and phrases: Brownian bridge, Diffusion process, Euler-Maruyama approximation, Gibbs algorithm, Incomplete data model, Maximum likelihood estimation, Non-linear mixed
When the transition density is unknown, we prove the convergence of a different version of the algorithm based on the Euler approximation of the SDE towards the maximum
Keywords: Approximate maximum likelihood, asymptotic normality, consistency, co- variates, LAN, mixed effects, non-homogeneous observations, random effects, stochas- tic
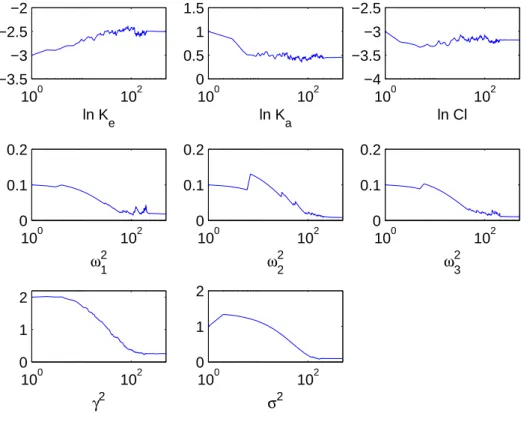
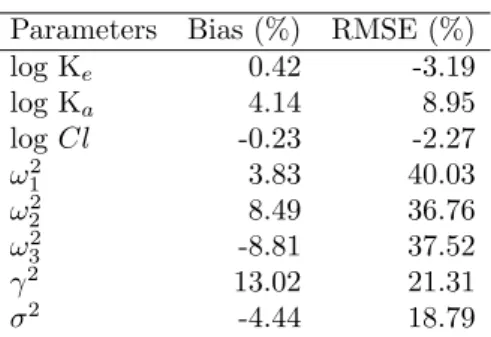
Test for 92 populations of 1000 individuals: Results (from Monolix) and errors for the mean parameters of the population.. Column E1 refers to a population
Section 2 further introduces notations through a general presentation of SDEs with mixed-effects as an extension of classical nonlinear mixed-effects models. The asymptotic
We consider here a parametric framework with distributions leading to explicit approximate likelihood functions and study the asymptotic behaviour of the associated estimators under