A bisimulation between DPLL(T) and a proof-search strategy for the focused sequent calculus
Texte intégral
Figure

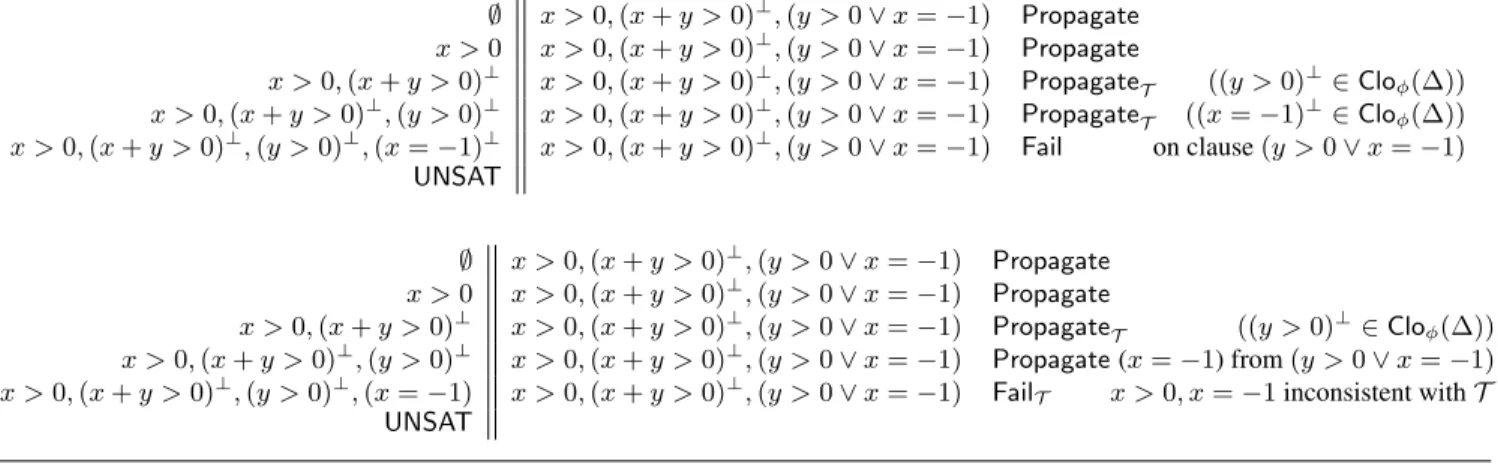
Documents relatifs
We find 50 miRNAs with significant target enrichment among genes highly expressed in 3 or more tissues, suggesting a pattern of mutual exclusivity between miRNA and
The application of the FSA score to foods in the French context indicated that the score could be used as a basis for a five-category system, provided marginal adjustments in a few
Figure 1 Regional tectonic map of the Tibetan plateau and station distribution of this study showing major su- ture zones, terranes, fault systems, the dip and plunge of the
We can expect (and it is indeed the case) that the combi- natorics of these objects is not easy to describe. In particular, a representation which is adapted to computer
The paper is organised as follows: Section 2 introduces the focused sequent calculus with polarities, Section 3 reviews the basic DPLL(T ) procedure [NOT05, BNOT06], Section 4
This paper ad- dresses the issues of dening such sequent calculi for Pure Type Systems (PTS, which are based on natural deduction) and then organizing their rules for ef- fective
– Plugins can be programmed to drive the kernel, using its API, through the search space towards an answer provable or not provable; soundness of the answer only relies on the
The sequent calculus LK (T ) manipulates the formulae of first-order logic, with the specificity that every predicate symbol is classified as either positive or negative, and