Maximum Flow and Minimum-Cost Flow in Multi-Interface Networks
Texte intégral
Figure
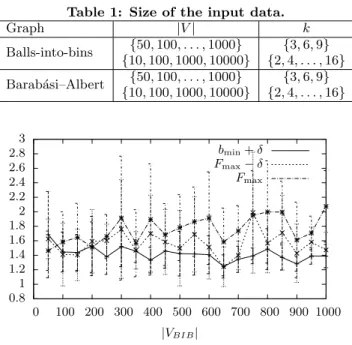

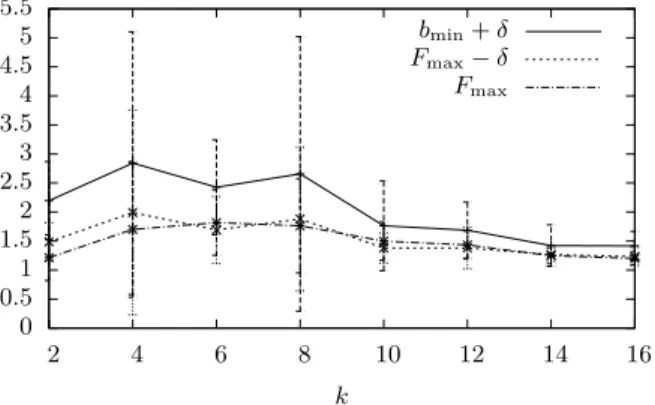
Documents relatifs
Our approach con- sists in an alignment of SysML concepts with an identified subset of the B method, using semantic similarities between both languages.. The obtained process is
We present a new method using the Successive Shortest Path (SSP) algorithm of smaller complexity to solve the minimum cost flow problem in a specific dynamic context.. Our
Viral genome fingerprints of sediment samples taken at different locations: marine (Øresund), brackish (Niv ˚a Bay) and freshwater (Lake Esrum and Lake Frederiksborg Slotssø)
We present stochastic particle approximations for the normalized Ricci flow on surfaces and for the non-normalized Yamabe flow on manifolds of arbitrary dimension.. Keywords: Ricci
• Rules A2-B2 ensure that all the data needed for an it- eration of the sub-graph are available as soon as its ex- ecution starts, and that no external vertex can consume on the
In the support of the integration approach, we have defined an information model [2] based on SysML language to address requirements definition and their
scale and to explore a SCO sample in a form probably closer from the applicative one, we present here the first study of the coherent domains morphology in a powder including