Optimal Step-Size Constant Modulus Algorithm
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
As for toric Fano manifolds, Galkin, Golyshev and Iritani([8]) proved Gamma con- jectures I, II modulo Conjecture O, and then Galkin ([6]) has made some progress on Conjecture O
While we have provided some theoretical arguments (asymptotic expansion in the finite-dimensional case, convergence to optimal predictions in the infinite- dimensional case), a
It combines indica- tor-based selection based on the contributing hypervolume with the efficient strategy parameter adaptation of the elitist covariance matrix adaptation
Trigonometric trinomial, maximum modulus, exposed point, ex- treme point, Mandel ′ shtam problem, extremal problem, relative Fourier multi- plier, Sidon constant,
In this contribution we use methods of optimal control theory to compute the optimal step length of the Newton method on the class of self-concordant functions, as a function of
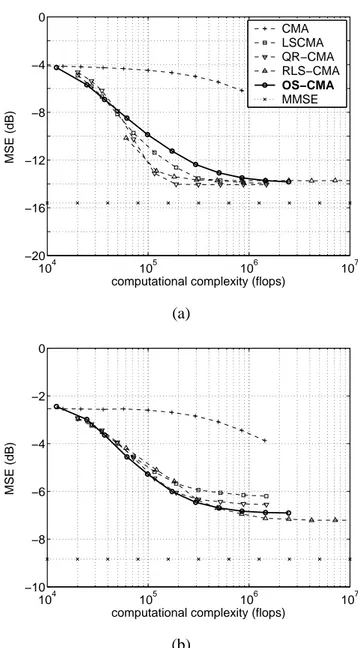
In particular, several adaptive algorithms have been pro- posed for the optimization of the Constant Modulus cost func- tion including the adaptive Analytical CMA (ACMA) in
the values of the p consecutive coefficients a,, a^ ..., dp are given with cip-^o^ there exists an upper limit to the moduli of the p roots of smallest absolute value which is
Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rennes, Irisa, Campus universitaire de Beaulieu, 35042 RENNES Cedex Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rhˆone-Alpes, 655, avenue de l’Europe, 38330 MONTBONNOT ST