Approaches to evaluate spatial and temporal variability of deep marine sediment characteristics under the impact of dense water formation events
Texte intégral
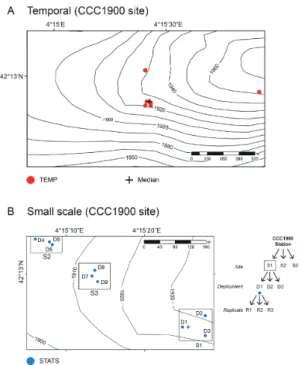
Figure


Documents relatifs
This slightly decreases the total transport in the Northern Hemisphere, but increases that in the Southern Hemisphere as the western boundary layer transport becomes smaller than
Enfin le chapitre VIII est consacré à la conception d'un schéma réactionnel susceptible de rendre compte de l'ensemble des transformations subies par les charbons durant
Probability distribution of impact velocities for the Moon and terrestrial planets... Relative cratering rate on the Moon for the current Earth-Moon distance and for crater
An R&D person might be the initial leader as the emerging technology is getting nurtured toward product form; later a marketing individual might take over as
Les résultats des moments et les déplacements maximaux ainsi que les principaux coefficients de sécurité, issus de l’approche combinée par l’application des
Ainsi, en fonction de l’état hydrique initial et du coefficient d’écoulement, les évènements pluvieux ont été séparés en deux groupes distincts (figure 4), pour lesquels
suggests five hotspots with column density higher than 20 × 10 15 molec cm −2 : Jing-Jin-Tang; combined southern Hebei and northern Henan; Jinan; the Yangtze River Delta; and
Percentage contribution in fluxes of total suspended sediment (TSS), total dissolved solid (TDS), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) of the total matter fluxes transported by the