Measurement of the top quark mass in the lepton+jets final state with the matrix element method
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Lebedev Physical Institute, Moscow, Russia 41: Also at California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA 42: Also at Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia 43: Also
Wikipedia: is a numerical technique that extends the dynamics of granular material or particles as described through the classical discrete element method (DEM)
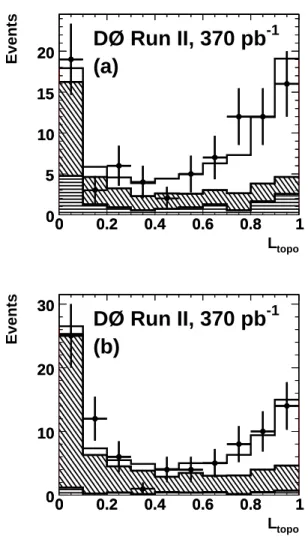
Since the systematic uncertainties are derived from simulation or data samples with limited numbers of events, all systematic uncer- tainties have a corresponding
36 ( a ) Department of Modern Physics and State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui, China; ( b ) School
33 ( a ) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China; ( b ) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
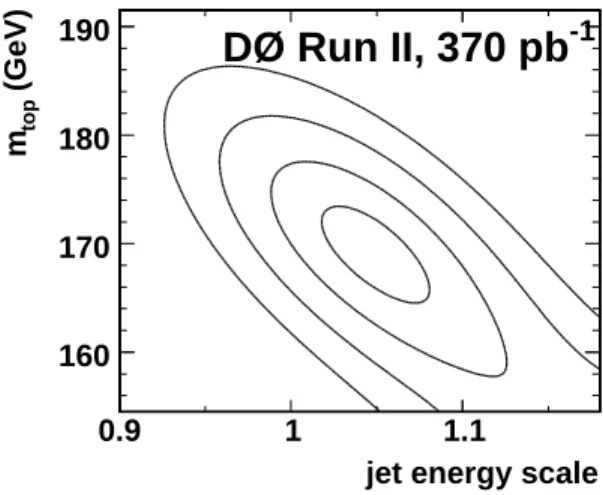
The method described above is checked for any possible systematic biases by running large numbers of ‘‘pseudoex- periments,’’ where we create, using Monte Carlo simula- tion,
Systematic uncertainties of the FCNC signal ac- ceptance relative to the acceptance of the lepton þ jets normal- ization mode and the background rate for the b-tagged and
A systematic uncertainty is estimated for each jet energy correction by performing Monte Carlo experiments drawn from simulated signal and background events with 1 standard deviation