A Ginzburg-Landau model with topologically induced free discontinuities
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
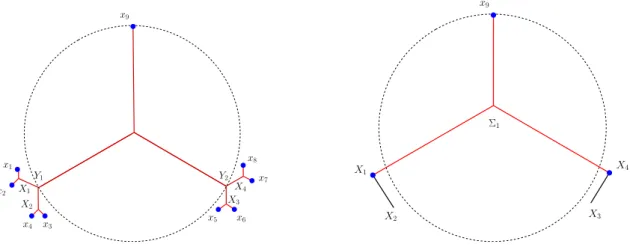
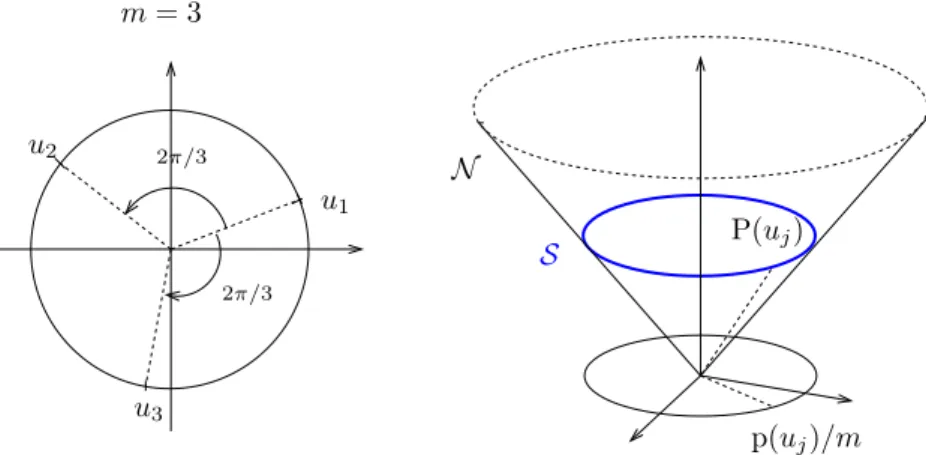
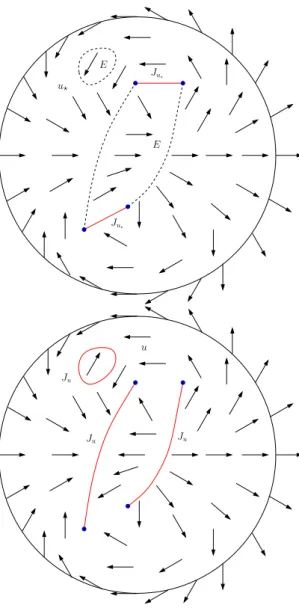
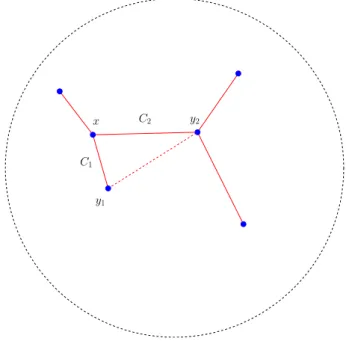
Once this done, in a second step, coupling energy estimates with an η-ellipticity result (see below) we get that the set where we have a concentration of the energy corresponds to
Shafrir, Minimization of a Ginzburg-Landau type energy de- creasing with potential having a zero of infinite order, en Differential Integral Equations 19, no.10, (2006), p. Struwe,
For sake of completeness, we give also the limit behaviour of the previous Ginzburg-Landau equation with homogeneous Dirichlet boundary condition (for scalar problems with
Factors influencing fecundity and population egg production of Jasus species.. Behaviour and sensory
The aim of this final section is to use the structure of the minimizers of the limiting functional F 0,g given by Theorem 4.3 to prove that minimizers of F ε,g 0 have the same
Lorsque y 1 < y 2 ( c'est à dire lorsque la variation absolue est un nombre positif ) , on parle d'augmentation ( ou de hausse ) ; dans ce cas, le taux d'évolution est positif
The stability region for the rhombic vortices, along with that for fundamental solitons, has been identified in the parameter space of the model, and generic scenarios of the
In conclusion, we investigate families of fundamental and vortical spatiotemporal dissipative solitons in the framework of the 3D CGL equation with the CQ nonlinearity,