Changing time and emotions
Texte intégral
Figure
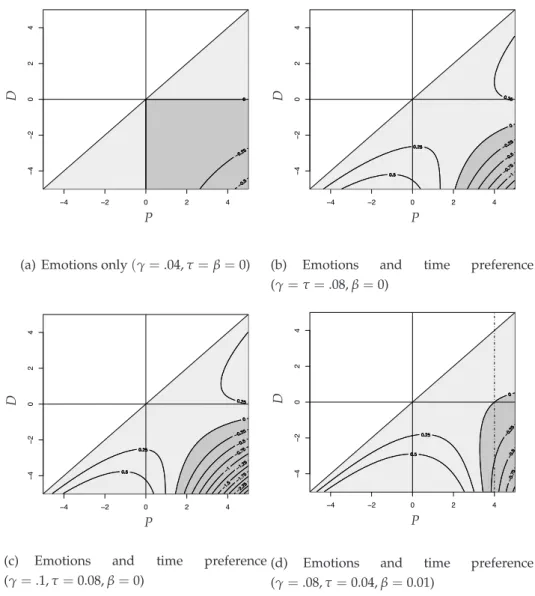
Documents relatifs
We show that the Tolman-Ehrenfest effect (in a stationary gravitational field, temperature is not constant in space at thermal equilibrium) can be derived very simply by applying
With the increase of milling time all Co atoms became dissolved in the bcc Fe and the final product of the MA process was the nanocrystalline Fe (Co) solid solution with a mean
In the same way one could argue that the B-theory of time is not a kind of anti- realism about time, for the very reason that the existence of A-properties is not
Since working memory (both epizodic and autobiographic) does not exist the brain is not able to model the self, and the patients loses an ability to in an insight into the
Nev- ertheless, the effects were different for the two conditions: the temporal context affected the estimates more in the implicit onset condition, and the estimates were more
Boredom was nevertheless correlated with the activity performed during the lockdown as well as the emotion felt (happiness and anxiety) and the level of arousal experienced (low-
The mass of carbon in the dissolved inorganic carbon reser- voir (DIC) may change as a function of the inputs of DIC from land via rivers, surface runoff and groundwater
It is based on an iterative algorithm and leads to an efficient approximation of Brownian hitting times for curved boundaries, and, by extension, can deal with diffusion