Asymmetric Hybrid Polymer-Lipid Giant Vesicles as Cell Membrane Mimics
Texte intégral
Figure
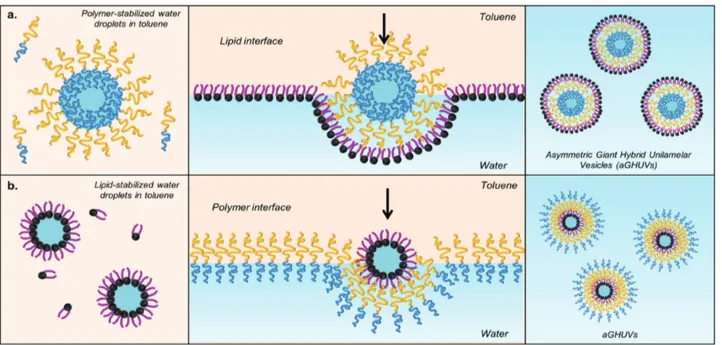
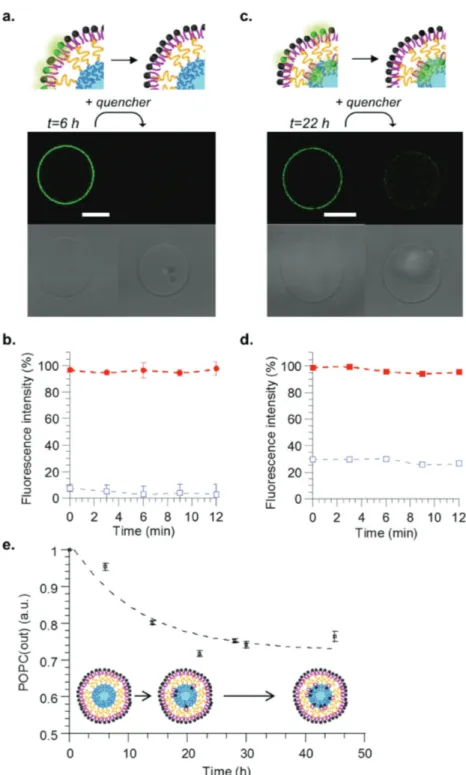
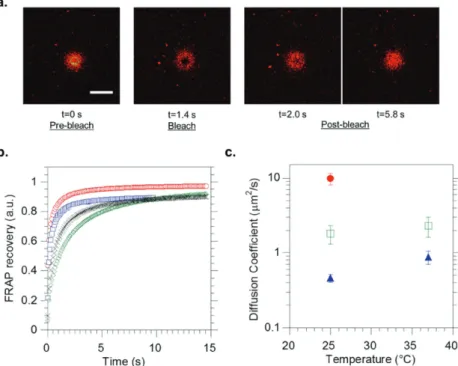
Documents relatifs
In this work, we studied in detail the formation and phase separation in the membranes of both Giant Unilamellar Hybrid Vesicles (GHUVs) and Large Unilamellar Hybrid
Modeling of the time dependence of the IR pyrometric signal allows simultaneously the determination of the layer thickness, the growth rate, surface roughness and refractive index
SPMD applications dynamically at a moderate hardware cost. DITVA extends an in-order SMT architecture by dynamically aggregating instruction instances from different threads
Coded time of flight cameras: sparse deconvolution to address multipath interference and recover time profiles.. The MIT Faculty has made this article
ةﺮﻐﺛ ﺪﺴﻳ درﺎﺴﻟا ﺪﳒ دارﺈﺑ ﻩ دﺮﺴﻟا ﻩزوﺎﲡ ثﺪﳊ ﻪﻋﺎﺟﱰﺳﺎﺑو ﺪﺼﻗ ﺔﻘﺑﺎﺳ ثاﺪﺣﺄﺑ ثﺪﳊا اﺬﻫ ﻂﺑﺮﺑ مﻮﻘﻳ ﺚﻴﺣ ﺔﻴﺼﺨﺸﻟا ﻲﺿﺎﳌ ًﺎﻀﻳأ لﻮﻘﻳو .ﺎﻬﻠﻳوﺄﺗ » ﻛﺮﺗ ﺖ ﻲﺴﻔﻨﻟ
Les pathologies du rachis chez l’enfant surviennent généralement en période pré pubertaire : vers 12 13 ans chez les filles (avant les premières règles), vers 13 14 ans
Here we report that color-biased cortex is sandwiched between face-selective and place-selective cortex on the bottom surface of the brain in humans. This face/color/place
• (Adaptive constraints) The optimization strategy (Conv) described in Algorithm 2 section §6.1, based on the hierarchy of cones Conv(V), and used in our numerical experiments