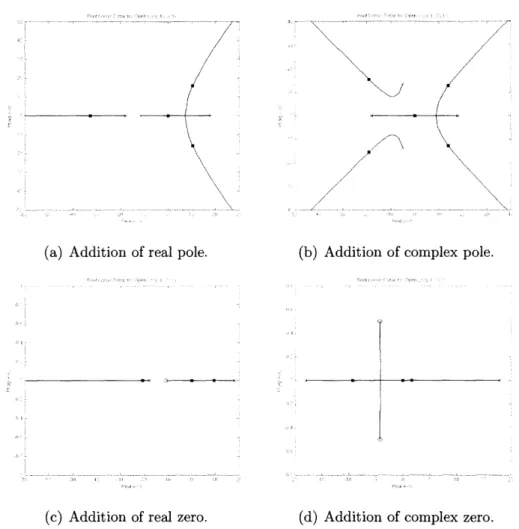
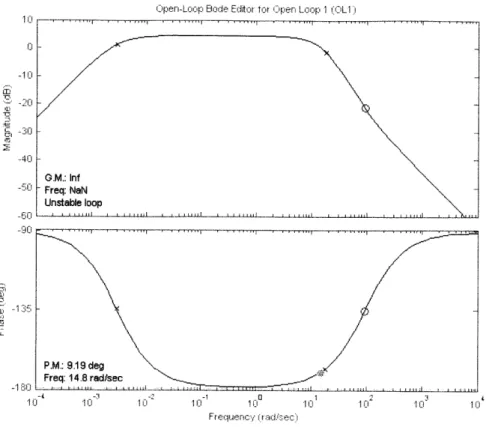
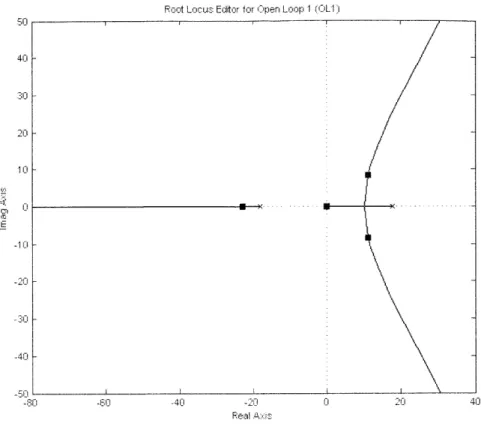
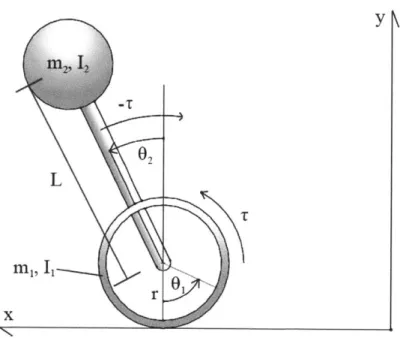
Balancing a two-wheeled Segway robot
Texte intégral
Figure


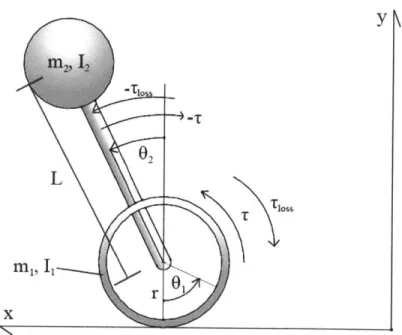
Documents relatifs
En 2010, 8 900 dossiers de candidature à la VAE ont été jugés recevables pour les titres professionnels du ministère chargé de l’emploi, soit 18 % de moins qu’en 2009 (tableau
Having evaluated a variety of tools used for some or all of the deployment activity, we now propose a reference architecture for deploying component-based robot software.. According
We have 10 unknowns for 6 equations: our robot has a second order hyperstatic equilibrium... A con fi guration where the middle wheel is
After that, based on the center of the obtained interval observer, a new control law is proposed to guarantee the tracking performance of the WMR despite the existence of
2) Faultload: As the functional layer communicates with the decisional layer via messages (requests and replies) trans- ferred using a Mail Box, robustness testing can be implemented
Here, we propose to mimic human motion based on critical points we extracted from human locomotion in order to control the biped robot to stand-up after a stable and dynamic
Indeed, the real-time BIP engine becomes a temporal plan execution controller by providing a correct schedule of actions, which communicates with the functional level through an
This work is in the context of the Digital Ocean Europe project that aims at digitalizing seafloor sites in 3D imagery using underwater robots (ROVs), and uses this