Complex Fluids and Hydraulic Fracturing
Texte intégral
Figure
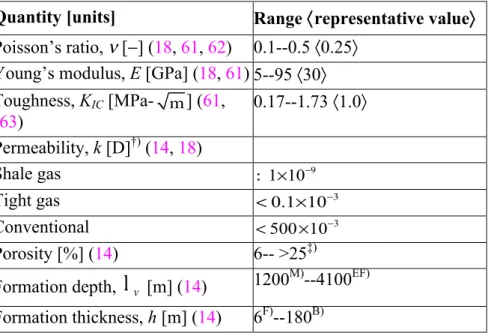
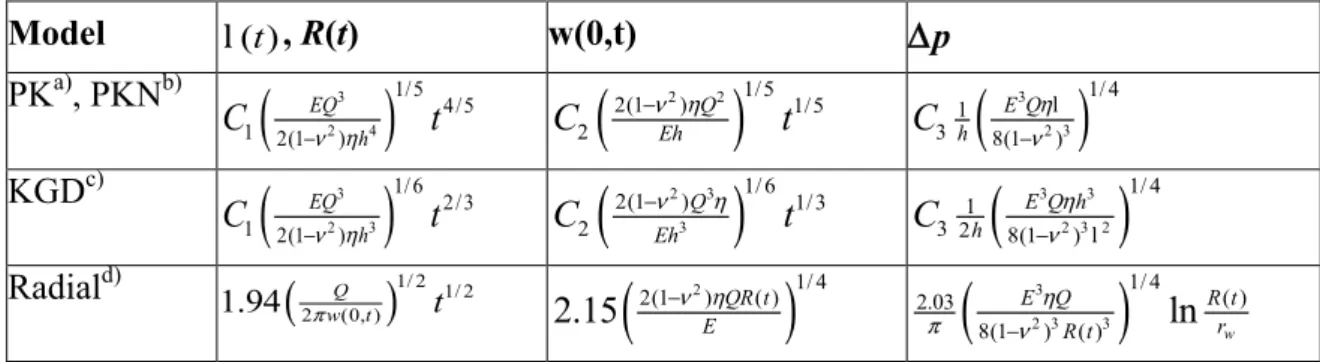
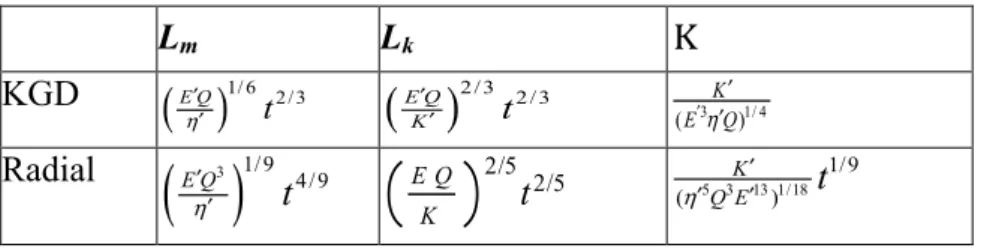
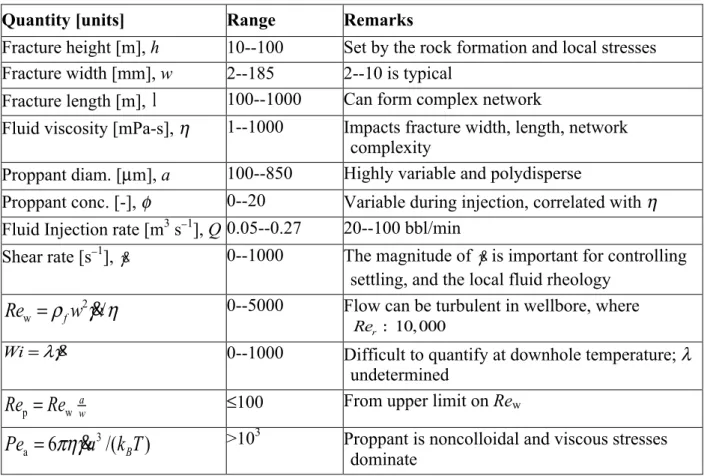
Documents relatifs
Simulation in different conditions (RT 60 = 100 ms–700 ms) illustrates the superiority of the proposed method over using beamforming or blind source separation alone; and
Assume further that the average interarrival time of fair ratings for a given seller is X and that personalized MREs R' (t) are based only on ratings for 5 submitted by buyers u
decreased systematically for all toughness cases supporting the idea that reliability and fracture toughness designate similar properties for service life or material resistance
Lifetime man- agement of underground pipelines is mandatory for safety and the use of HDPE tubes subjected to internal pressure, external loading and environmental
In nature ice more often than not contains cracks, and so the question arises: Does the fracture of cracked ice occur through the propagation of a pre-existing crack once the
Analytic solutions from linear elastic fracture mechanics for three fracture models (PKN, KGD and radial fracture geometry) are coupled with a general contact law
Although the literature dealing with the problem of hypothesis testing of decision type is very rich the application of this body of knowledge to model selection
The characterization of the main fracture sets allow the modeling of a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network) in the reservoir and the modeling of the derived hydraulic properties that