Publisher’s version / Version de l'éditeur:
Vous avez des questions? Nous pouvons vous aider. Pour communiquer directement avec un auteur, consultez la première page de la revue dans laquelle son article a été publié afin de trouver ses coordonnées. Si vous n’arrivez pas à les repérer, communiquez avec nous à PublicationsArchive-ArchivesPublications@nrc-cnrc.gc.ca.
Questions? Contact the NRC Publications Archive team at
PublicationsArchive-ArchivesPublications@nrc-cnrc.gc.ca. If you wish to email the authors directly, please see the first page of the publication for their contact information.
https://publications-cnrc.canada.ca/fra/droits
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE WEB.
Fire Study (National Research Council of Canada. Division of Building Research), 1974-11-01
READ THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE USING THIS WEBSITE. https://nrc-publications.canada.ca/eng/copyright
NRC Publications Archive Record / Notice des Archives des publications du CNRC : https://nrc-publications.canada.ca/eng/view/object/?id=69fc56cf-58f4-4191-a513-85d02e2ab941 https://publications-cnrc.canada.ca/fra/voir/objet/?id=69fc56cf-58f4-4191-a513-85d02e2ab941
NRC Publications Archive
Archives des publications du CNRC
For the publisher’s version, please access the DOI link below./ Pour consulter la version de l’éditeur, utilisez le lien DOI ci-dessous.
https://doi.org/10.4224/40001356
Access and use of this website and the material on it are subject to the Terms and Conditions set forth at
Experimental study on behaviour of structural elements made of
hot-rolled and cold-formed steels in fire
NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL O F CANADA DIVISION O F BUILDING RESEARCH
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON BEHAVIOUR O F STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS MADE O F
HOT-ROLLED AND COLD-FORMED S T E E L S IN FZRE
by L. Konicek F i r e Study No. 35 of the D i v i s i o n of Building R e s e a r c h OTTAWA November 1974
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON BEHAVIOUR OF STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS MADE OF
HOT-ROLLED AND COLD-FORMED STEELS IN FIRE
L. Konicek
ABSTRACT
Two types o f open-web s t e e l j o i s t s have been designed f o r t h e same span and t h e same loading conditions. The f i r s t type of j o i s t was made of h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l shapes. Cold- formed s t e e l was used f o r c o n s t r u c t i o n of t h e second type.
The
e f f e c t of t h i s d i f f e r e n c e on t h e behaviour of j o i s t s exposed t o f i r e , i s i n v e s t i g a t e d i n t h i s experimental study.
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON BEHAVIOUR OF STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS MADE OF
HOT-ROLLED AND COLD-FORMED STEELS IN FIRE
L . Konicek
I d e n t i c a l r o o f assemblies supported by a p a r t i c u l a r t y p e of s t e e l j o i s t were b u i l t . Each o f them was t e s t e d according t o "Standard f o r F i r e T e s t s o f Building Construction and ~ a t e r i a l s "
.
'
Results o b t a i n e d , t h e i r e v a l u a t i o n , and a comparison of t h e behaviour of both samples t e s t e d , a r e p r e s e n t e d i n t h i s r e p o r t .SPECIFICATIONS OF MATERIALS USED
1. Open-web s t e e l j o i s t , 16 i n . deep ( h o t - r o l l e d chords) S t e e l : Chord, G 40.12
Web, A 36
Applied load s p e c i f i e d by manufacturer, 1020 p l f T o t a l c r o s s - s e c t i o n a r e a o f chords, 1.920 i n . 2 Weight, 8.9 l b / f t
For d e t a i l s e e Figure 1.
2. Open-web s t e e l j o i s t , 16 i n . deep (cold-formed chords)
S t e e l : Yield s t r e n g t h , 55000 p s i
T e n s i l e s t r e n g t h , 67000 p s i , minimum
Applied load s p e c i f i e d by manufacturer, 1138 p l f T o t a l c r o s s - s e c t i o n a r e a o f chords, 1.868 i n . 2 Weight, 7.7 l b / f t
For d e t a i l s s e e Figure 2.
3 . Roof deck: 6 f t 2 i n . countersunk one end t o provide l a p j o i n t
3 f t 7 i n . countersunk one end t o provide l a p j o i n t
3 f t 7 i n . p l a i n ends
Units f a b r i c a t e d from 16-gauge wiped coated (galvanized) s h e e t s t e e l
4. Thermal i n s u l a t i o n : 1 - i n . o r g a n i c f i b r e i n s u l a t i n g board
5. F i r e p r o t e c t i o n : Cementitious sprayed p r o t e c t i o n , t h i c k n e s s 2 i n . average d e n s i t y 16.2 l b / f t 3 .
CONSTRUCTION OF A ROOF ASSEMBLY
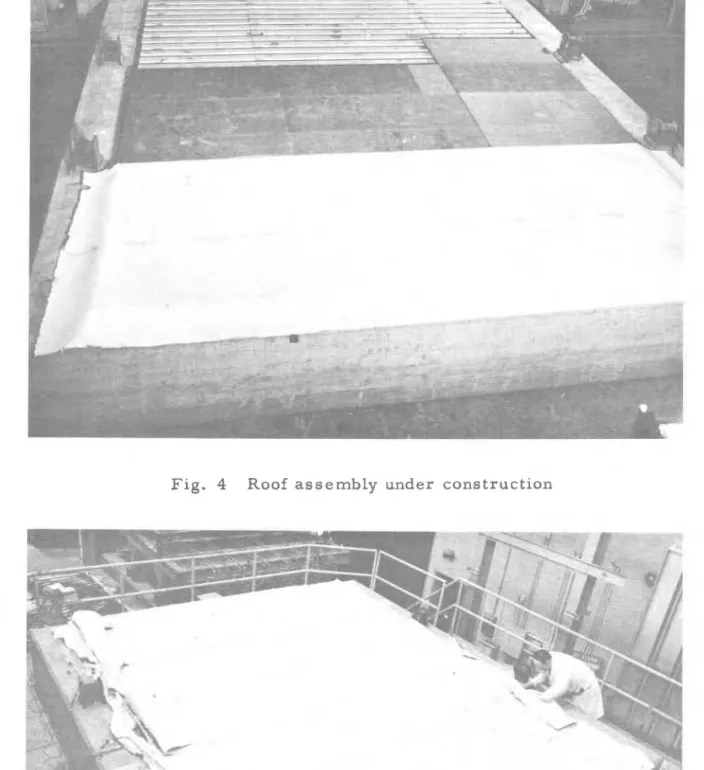
Two simply-supported open-web s t e e l j o i s t s were placed i n t h e c o n c r e t e frame which forms p a r t o f t h e f l o o r furnace. An arrangement of j o i s t s i n t h e frame with d e t a i l o f j o i s t b r a c i n g and support can b e s e e n i n Figure 3 . The s t e e l roof deck was plug welded t o t h e s u p p o r t i n g s t r u c t u r e and covered by thermal i n s u l a t i o n with a s b e s t o s paper on i t s e x t e r n a l s u r f a c e . The method o f c o n s t r u c t i o n of t h i s p a r t of t h e assembly can be s e e n i n Figure 4 . The unprotected roof deck i s shown a t t h e t o p o f t h e p i c t u r e , t h e roof deck p r o t e c t e d by thermal i n s u l a t i o n i n t h e middle, and t h e completed e x t e r n a l s u r f a c e o f t h e r o o f a t t h e bottom and i n Figure 5 .
The thermocouples were peened t o t h e s u r f a c e of open-web s t e e l j o i s t s i n p r e s c r i b e d p l a c e s ( s e e Figure 6 ) and a t t a c h e d by screws t o t h e s t e e l roof deck ( s e e Figure 7 ) . S u r f a c e temperatures on t h e unexposed s i d e were measured by a s e t o f thermocouples covered by s t a n d a r d a s b e s t o s pads ( s e e Figure 8)
.
A f t e r mounting a l l thermocouples and s t r a i n gauges, t h e s u r f a c e o f t h e c o n s t r u c t i o n exposed t o f i r e was sprayed with cementitious f i r e p r o t e c t i o n . Incomplete f i r e p r o t e c t i o n o f t h e assembly can be s e e n i n Figure 9 . The
completed assembly i s shown i n Figure 10.
A f t e r c a r e f u l c u r i n g , during which t h e moisture c o n t r o l i n t h e sprayed f i r e p r o t e c t i o n reached a s t e a d y l e v e l , with only very small weight d e v i a t i o n s
(caused by v a r i a t i o n i n t h e r e l a t i v e humidity of t h e a i r i n t h e l a b o r a t o r y ) , t h e assembly was ready f o r t e s t i n g . The changes i n d e n s i t y o f t h e sprayed f i r e p r o t e c t i o n i n r e l a t i o n t o time a r e p l o t t e d i n Figure 11. Both completed roof assemblies were s t o r e d i n t h e l a b o r a t o r y f o r approximately two months p r i o r t o t h e f i r e t e s t s .
INSTRUMENTATION
Furnace temperature was measured by n i n e chromel-alumel thermo-
couples enclosed i n s t a n d a r d weight 1 / 2 - i n . black wrought-iron p i p e . I n d i v i - dual temperatures, a s well a s t h e average recorded temperature o f t h e n i n e thermocouples, were recorded.
A t y p i c a l arrangement of thermocouples measuring t h e temperature
course i n an open-web s t e e l j o i s t c r o s s - s e c t i o n can be s e e n i n Figure 6 . The l o c a t i o n s o f t h e s e t y p i c a l c r o s s - s e c t i o n s A-F a r e shown i n t h e s k e t c h o f t h e roof assembly p l a n , a g a i n i n Figure 6 .
Temperatures on t h e s t e e l r o o f deck were measured i n l o c a t i o n s G and H by thermocouples 1-4 ( s e e Figure 7 )
.
Unexposed s u r f a c e temperatures were measured a t n i n e l o c a t i o n s shown i n Figure 8; t h e thermocouples were covered with s t a n d a r d a s b e s t o s pads.
S t r a i n on t h e loaded c o n s t r u c t i o n was measured b e f o r e t h e f i r e t e s t , by s t r a i n gauges, which were a t t a c h e d t o t h e upper chord, t h e lower chord and t h e diagonal o f each j o i s t , i n t h e middle o f i t s span. This measurement, t o g e t h e r with measured d e f l e c t i o n s a t t h i s s t a g e o f t h e experiment, proved c o r r e c t load d i s t r i b u t i o n .
The load permitted by t h e manufacturer's s p e c i f i c a t i o n was a p p l i e d by means of 30 h y d r a u l i c jacks.
V e r t i c a l d e f l e c t i o n s were measured a t t h e c e n t r e of each open-web s t e e l j o i s t and i n t h e middle o f t h e t e s t e d r o o f assembly.
FIRE TESTS AND READINGS
The furnace temperature s a t i s f a c t o r i l y approached t h e s t a n d a r d time-temperature curve1 throughout both t e s t s ( s e e Table 1 and Figure 1 2 ) . Maximum d e v i a t i o n was always w i t h i n t h e p e r m i s s i b l e l i m i t s and no c o r r e c t i o n f a c t o r was r e q u i r e d .
Temperatures measured on t h e assembly made o f h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l a r e p r e s e n t e d i n Table I1 and Figure 13. When a reading on a thermocouple was h i g h e r a t one l o c a t i o n than a t another comparable l o c a t i o n ( f o r example
A = 1 6 2 5 ' ~ ) ~ t h e r e a d i n g was marked on t h a t p a r t i c u l a r Table, and p l o t t e d i n t h e corresponding f i g u r e a s a course o f maximum temperature i n t h e measured p l a c e .
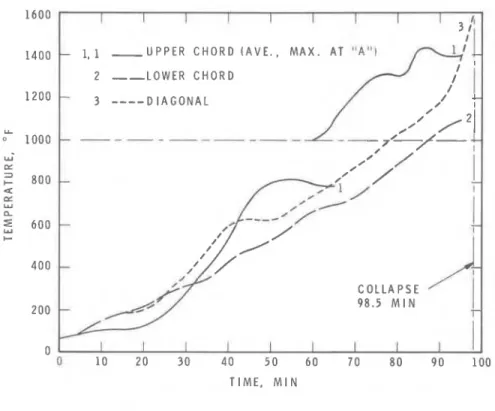
D e f l e c t i o n measurements f o r t h e l1Northl1 open-web s t e e l j o i s t u s i n g h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l a r e shown i n Table I11 and Figure 14. The j o i s t c o l l a p s e d a t 98.5 min.
The d a t a o b t a i n e d from t h e f i r e t e s t o f t h e r o o f assembly, where cold-formed s t e e l i s used i n t h e c o n s t r u c t i o n o f t h e s t e e l j o i s t s , a r e s i m i l a r l y p r e s e n t e d . Temperatures a r e shown i n Table IV and Figure 15; d e f l e c t i o n s a r e i n Table I11 and Figure 14. The "North" j o i s t c o l l a p s e d a t 95.5 min.
A p a r t i c u l a r comparison o f measured d e f l e c t i o n s on open-web s t e e l j o i s t s made o f cold-formed s t e e l and h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l was made and i t s ' r e s u l t s can b e found again i n Table I11 and Figure 14.
OBSERVATIONS
Thermal p r o t e c t i o n of both assemblies was checked b e f o r e t h e f i r e t e s t s . There was no v i s i b l e damage i n t h e f i r e p r o t e c t i o n .
During t h e f i r s t hour o f t h e f i r e t e s t s no change i n t h e q u a l i t y o f t h e f i r e p r o t e c t i o n was n o t i c e d . L a t e r on, s e v e r a l very t h i n cracks were observed. Some o f t h e cracks began t o develop a t 40 min, a s i n d i c a t e d by
s e v e r a l thermocouple r e a d i n g s .
A f t e r 70 minutes s e v e r a l cracks developed t o a much l a r g e r e x t e n t . These d i s t u r b a n c e s caused t h e roof assembly using h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l t o c o l l a p s e a f t e r 98.5 min. The assembly using cold-formed s t e e l withstood 95.5 min o f f i r e t e s t . D e t a i l s o f t h e c o l l a p s e d roof assemblies a r e shown i n Figure 16 (a) t o (e)
.
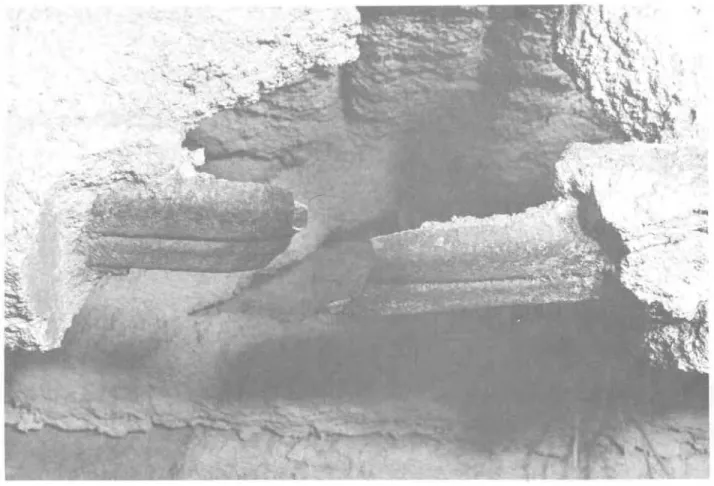
A p i c t u r e o f t h e s u r f a c e o f t h e roof assembly exposed t o t h e f i r e t e s t i s shown i n Figure 16 ( a ) . D e t a i l of t h e ruptured lower chord o f t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t i s i n Figure 16 ( b ) . Deformed s t r u c t u r a l s t e e l and r e s u l t i n g r u p t u r e o f t h e lower chord o f t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t i s shown i n Figure 16 (c)
,
(d),
and (e).
Figure 16 (a) t o (e) shows t h e r u p t u r e d open-web s t e e l j o i s t where h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l was used. Figure 17 shows a r u p t u r e d lower chord o f open-web s t e e l j o i s t made o f cold-formed s t e e l .When sprayed f i r e p r o t e c t i o n was taken o f f t h e j o i s t s a f t e r t h e f i r e t e s t s , t h e s u r f a c e o f t h e j o i s t s was corroded. Figures18 and 19 show t h e change i n c o l o u r o f t h e s u r f a c e o f t h e sprayed p r o t e c t i o n i n c o n t a c t with t h e s t e e l ( t o p p a r t of Figures 18 and 1 9 ) . Samples with marks o f c o r r o s i o n a r e compared t o a sample not exposed t o t h e f i r e t e s t (lower p a r t o f Figures 18 and 1 9 ) .
RESULTS
I n t h e case o f t h e assembly u s i n g h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l , t h e average temperatures measured on t h e lower chord, upper chord and diagonals of t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t , reached t h e ASTM c r i t i c a l s t e e l temperature,
-
tc
-
1 1 0 0 ° ~ , a f t e r 80 min. The c r i t i c a l temperature was exceeded i n s e v e r a l p l a c e s much sooner ( s e e Figure 13, Table 1 1 ) . Actual c o l l a p s e occurred a t 98.5 min, (when t h e lower chord o f t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t r u p t u r e d . )The temperature measured on t h e upper chord of t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t made o f cold-formed s t e e l reached i t s c r i t i c a l v a l u e i n 60 min. Maximum measured temperatures i n p l a c e A ( s e e Figure 15) exceeded llOO°F a t 60 min o f t h e f i r e t e s t . A r u p t u r e o f t h e lower chord occurred a t 95.5 min.
The d e f l e c t i o n s on an open-web s t e e l j o i s t made o f cold-formed s t e e l were b i g g e r t h a n those measured f o r t h e h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l j o i s t . The measured d e f l e c t i o n values with p a r t i c u l a r comparisons a r e given i n Table
I11 and Figure 14.
During t h e t e s t s described i n t h i s r e p o r t , t h e formation of l a r g e cracks caused a s t e e p i n c r e a s e i n l o c a l s t e e l temperatures. The load- bearing c a p a c i t y o f t h e s t e e l was decreased with r e s u l t i n g r u p t u r e of lower chords f o r both t e s t e d open-web s t e e l j o i s t s .
CONCLUSION
The t e s t s have shown t h e following r e s u l t s :
Measured d e f l e c t i o n s i n t h e middle o f t h e span on t h e open-web s t e e l j o i s t s made o f cold-formed s t e e l were g r e a t e r t h a n corresponding d e f l e c t i o n s of open-web s t e e l j o i s t s made of h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l .
T o t a l c o l l a p s e of a j o i s t made o f cold-formed s t e e l came a t 95.5 min; a j o i s t made of h o t - r o l l e d s t e e l c o l l a p s e d a t 98.5 min. This d i f f e - rence is s o small t h a t performance o f both j o i s t s can be r a t e d e q u a l .
On t h e b a s i s of t h e s e r e s u l t s we can conclude t h a t t h e r e i s no s i g n i f i c a n t d i f f e r e n c e i n t h e performance of open-web s t e e l j o i s t s made of h o t - r o l l e d o r cold-formed s t e e l s when exposed t o f i r e . The f i r e r e s i s t a n c e c l a s s i f i c a t i o n of both assemblies according t o ASTM El19 was 1-1/2 h r .
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This p r o j e c t was undertaken a t t h e request o f t h e S t e e l I n d u s t r i e s Fellowship Committee. The work was c a r r i e d o u t under a cooperative program between DBR/NRC and t h e Canadian S t e e l I n d u s t r i e s Construction Council, known a s t h e S t e e l I n d u s t r i e s Agreement.
The author wishes t o thank Messrs. J . E . Berndt and E.O. Porteous, who c a r r i e d o u t t h e f i r e t e s t s and a s s i s t e d i n a n a l y s i s of t h e d a t a developed.
REFERENCE
1. Standard f o r F i r e T e s t s of Building Construction and ASlM El19 Materials, Second Edition, September 1971,
T A B L E I
FURNACE TEMPERATURES,
PRESCRIBED A ~ D EXPERIMENTAL
*
TIME,PRESCRIBED EXP.
-
HOT-ROLLED E X P .-
COLD-FORMED min. S T E E L S T E E LT A B L E I1
T E M P E R A T U R E S ON HOT-ROLLED S T E E L O P E N - W E B JOIST (AVERAGE, MAXIMUM)
( s e e Fig. 13)
T.EMP JOIST "SOUTH"
U P P E R LOWER U P P E R 1 LOWER DmGONAL DIAGONAL CHORD . - CHORD I 0 70 7 0 70 70 70 70 40 49 0
-
490 525 6151
580 560 5305
6
0
690 610 50 620 725 730 825 7 60 9 50 5 5 550 8 50 850 825 - I 790 900 60 560 975 860 79O -, ' 820 8 2 5 I 6 5 8001
A ~ 1 0 6 0 880 700 870 7 60 830 I 70 0 A31160 70'
5300
."10-k--600looo
,
7 50 Az1260 7 5 940 9 70I
790 9 80 I 8 0 8 5 1060 1120 1150 1325 I 90 9 5 h 1 3 3 0 1 I 1110 8751
1 0 6 01
850 950i
A=1625)
1250 12801
,
1 0 7 51
1085 A r 1525 1135 I 12251
ziioo
1220 - 1100 9 60 1180 A t 1600 1220 I 1340i
TABLE 111
DEFLECTIONS ON OPEN-WEB S T E E L JOISTS,
WHERE COLD-FORMED AND HOT-ROLLED S T E E L S ARE USED,
COMPARISON WITH CALCULATED DIFFERENCE
*
TIME DEFLECTION DEFLECTION
( min) COLD-FORMED S T E E L HOT-ROLLED S T E E L DIFFERENCE
0. 60 0.73 0. 82 0. 87 0.89 0. 89 0. 89 0.93 1.02 1.14 1. 31 1.54 1.72 2.02 2. 18 2.42 2.94 3. 83 5. 44 COLLAPSE 9 5. 5 min 0.80 0.80 0. 81 0.85 0.94 1.08 1.22 1.41 1. 56 1. 82 2.04 2. 24 2.48 3.04 COLLAPSE 98. 5 min - . -. - - --
*
s e e Fig. 14T A B L E IV
TEMPERATURES ON COLD-FORMED OPEN-WEB S T E E L JOISTS (MAXIMUM T E M P E R A T U R E )
*
J O I S T PARAMETERS S U P P L I E D B Y PRODUCER S P A N : 1 5 ' - 6 " W = 1 0 2 0 PLF STEEL: C H O R D S - G 4 0 . 1 2 F I G U R E 1 S K E T C H O F H O T - R O L L E D O P E N - W E B STEEL J O I S T W I T H TECH N l C A L PARAMETERS
J O I S T PARAMETERS SUPPLIED BY PRODUCER S P A N : 1 5 ' 6 " W = 1 1 3 8 P L F R R = R L = 8 8 2 0 L B STEEL: T E N S I L E S T R E N G T H : 6 7 0 0 0 PSI M I N I M U M Y I E L D S T R E N G T H : 5 5 0 0 0 P S I M I N I M U M F I G U R E 2 2 A6 = 1 . 0 3 2 ( I N . ) A 5 = 0 . 8 3 6 ( I N . 2 ) SKETCH O F C O L D - F O R M E D O P E N - W E B STEEL J O I S T W I T H T E C H N I C A L PARAMETERS
D E T . 1
h
S U P P O R T O F STEEL R O O F D E C K - -t
.I__- A S B E S T O S PAPER T H E R M A L I N S U L A T I O N STEEL R O O F D E C K J O I S T T H E R M A L I N S U L A T I O N S U P P O R T O F J O I S T S C O N C R E T E F R A M E W A L L O F T H E F U R N A C E TESTED STEEL J O I S T t --- --* - - - A Q ---- C O N T O U R O F S P R A Y E D FIRE P R O T E C T I O N O F STEEL PARTS S U P P O R T O F STEEL R O O F D E C K---
F R A M E O F THC F U R N A C E D E T . 1 F I G U R E 3 l-
h A S B E S T O S PAPER T H E R M A L I N S U L A T I O N STEEL R O O . F D E C K D E T . i L O C A T I O N O F J O I S T S I N THE F U R N A C E W I T H T W O D E T A I L S O F R O O F A S S E M B L Y ( S K E T C H )Fig. 4 Roof a s s e m b l y under c o n s t r u c t i o n
7 -
-I
PLAN OF T H E RGOF ASSEMBLY
-
TEMPERATURE I N L O C A T I O N S A-F WERE RECORDEDCROSS
-
SECTICN A-F WITH THERMOCGUPLES 1-
4'r"
NORTH
FIGURE 6
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT O N S T E E L J O I S T . L O C A T I O N O F THERMOCOUPLES
PLAN OF THE ROOF ASSEMBLY
-
NORTHS T E E L ROOF DECK CROSS SECTION
FIGURE 7
NORTH
L
FIGURE 8
F i g . 9 Uncompleted s p r a y e d f i r e protection of roof a s s e m b l y
1 0 0 4 8 1 2 16 20 24 28 32 36 N U M B E R O F D A Y S I I I 1 1 I I I S P R A Y E D F I R E P R O T E C T I O N : - 2" T H I C K N E S S O F M E A S U R E D S A M P L E - + - - - - - - - - L I 1 I I I I I I F I G U R E 1 1 C H A N G E I N D E N S I T Y O F S P R A Y E D M A T E R I A L W I T H R E L A T I O N T O T I M E
-
P R E S C R I B E D F U R N A C E T E M P E R A T U R E E X P E R I M E N T A L T E M P E R A T U R E , H O T R O L L E D S T E E L--
E X P E R I M E N T A L T E M P E R A T U R E , C O L D - F O R M E D S T E E L 30 4 0 5 0 6 0 T I M E , M I N F I G U R E 12 F U R N A C E T E M P E R A T U R E S . P R E S C R I B E D A N D E X P E R I M E N T A L0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 0 1 0 0 T I M E , M I N 1.1
-
U P P E R C H O R D ( A V E . , M A X . A T " A " ) 2--
LOWER C H O R D 3----
D I A G O N A L F I G U R E 1 3 T E M P E R A T U R E M E A S U R E D O N N O R T H O P E N - W E B STEEL J O I S T ( H O T - R O L L E D STEEL) I I I DEFLECT1 O N S I + C O L D F O R M E D STEEL I I -----
H O T R O L L E D STEEL-
I I I I I I 0 10 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 0 100 T I M E , M I N F I G U R E 1 4 D I A G R A M C O M P A R I N G T H E D E F L E C T I O N S OF C O L D - F O R M E D A N D H O T - R O L L E D O P E N - W E B STEEL J O I S T S0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 T I M E , M I N - 1, 1 U P P E R C H O R D ( A V E . , M A X . A T " A 1 0 2 --LOWER C H O R D T 3
----
D I A G O N A L * - - - - - - - - I - - 98.5 M I N 1- I 1 I I I I I I I F I G U R E 15 T E M P E R A T U R E M E A S U R E D O N N O R T H C O L D - F O R M E D S T E E L O P E N W E B J O I S T(a) Exposed surface of the assembly after fire test
( b ) D e t a i l of r u p t u r e d l o w e r c h o r d of s t e e l j o i s t
( c ) D e t a i l s of r u p t u r e d l o w e r c h o r d of o p e n - w e b s t e e l j o i s t
( d ) Change in d i m e n s i o n s of lower chord c r o s s - s e c t i o n a f t e r f i r e t e s t
( e ) Detail of r u p t u r e d lower chord of open-web s t e e l joist
Fig. 17 Deformation and r u p t u r e of open-web s t e e l joint made of cold-formed s t e e l
Fig. 1 8 C o r r o s i o n of s t e e l j o i s t , hot-rolled s t e e l .
F i r e p r o t e c t i o n with visible m a r k of c o r r o s i o n , w h e r e in contact with s t e e l ( t o p p i c t u r e ) . F i r e p r o t e c t i o n not exposed t o f i r e ( l o w e r p i c t u r e )
Fig. 19 Corrosion of s t e e l joist