Application of the multiresolution wavelet representation to non-cooperative target recognition
Texte intégral
Figure
![Figure 4. Example of wavelet functions used in 1-D discrete wavelet transforms – Daubechies family wavelets [10]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11602504.299556/3.892.465.837.864.1015/figure-example-wavelet-functions-discrete-transforms-daubechies-wavelets.webp)

Documents relatifs
We present a construction of biorthogonal wavelets using a compact operator which allows to preserve or increase some properties: regularity/vanishing moments, parity,
The semiconcavity of a value function for a general exit time problem is given in [16], where suitable smoothness assumptions on the dynamics of the system are required but the
The Craya decomposition can be generalized to a number of dimensions higher than three, distinguishing a preferential two-dimensional divergence-free vector space, then a
The situation is analogous to the one in Riemannian geometry with cut and conjugate points: Up to some point, the path provides minimizers; then global optimality is lost
The representation system of spatial entities and relations whose main lines we explain here has been used to give a formal definition to the prepositions dans 'in' and sur 'on'
One of the objectives of this study is to answer this question by proposing a complete approach, allowing for the development of numerical techniques based on the Double Modal
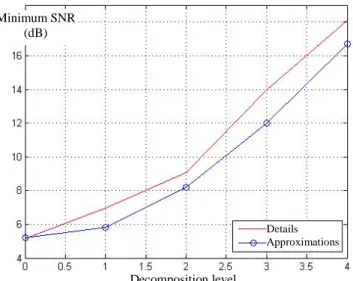
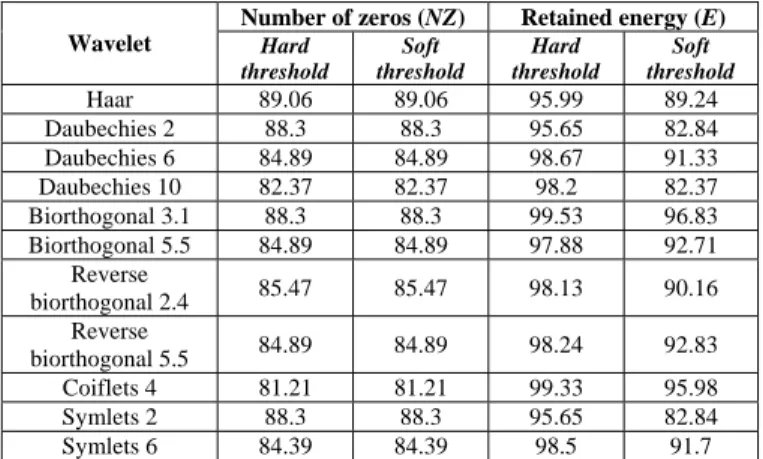
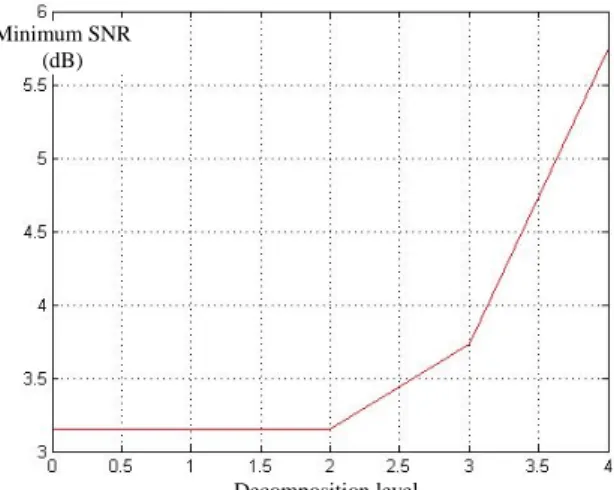
2) Probability distribution of the distance measurement error: Until now, degree of membership to a class k has been described through the distance between two range profiles.
Traversal time (lower graph) and transmission coefficient (upper graph) versus the size of the wavepacket for three different values ofthe central wavenumber, k = 81r/80 (dashed