Enhancement of genomic instability by 17[beta]-estradiol in minisatellite sequences of X-ray-transformed mouse 10T1/2 cells
Texte intégral
Figure
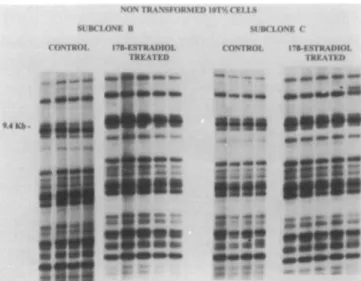
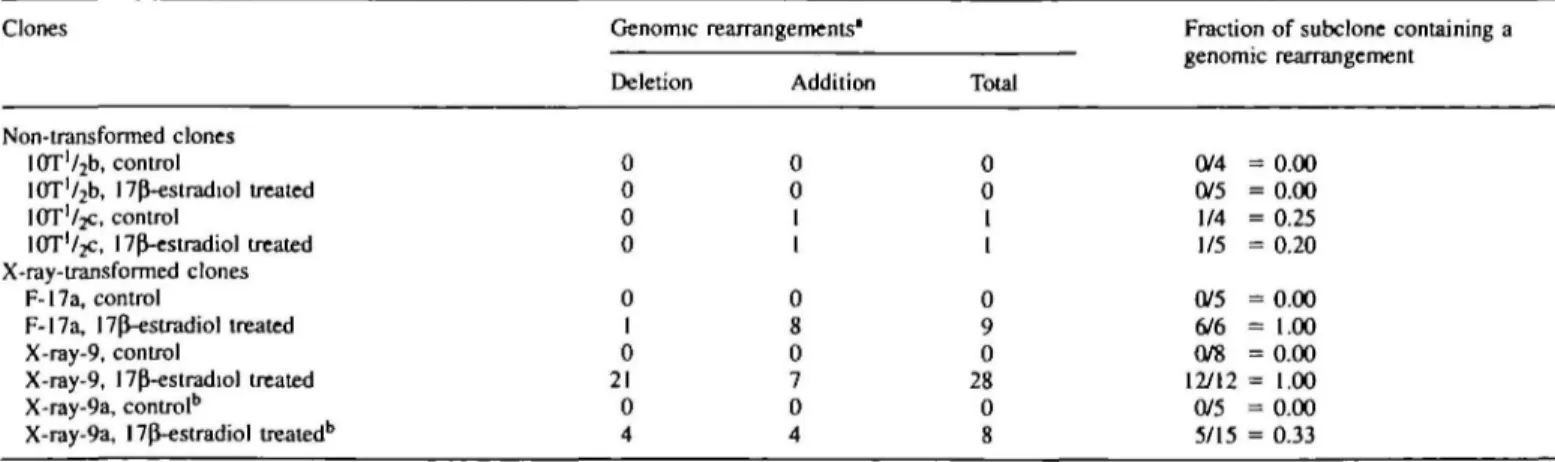
Documents relatifs
D’autres études sont nécessaires afin de mieux comprendre les conditions abiotiques des différents sites d’action des antibiotiques dans le corps humain, mais
Résolution par la méthode de relaxation d'un problème de contrôle optimal avec une entrée libre 7.1 Introduction Dans ce chapitre, nous présentons une méthode pour
This requirement of NUD1 for exit from mitosis is at least in part due to its function in recruiting MEN components to SPBs because binding of Tem1 and Cdc15 to SPBs is essential
(B) Representative 8% PAGE gel showing Rho helicase reaction products obtained under different reaction conditions with a tripartite RNA-DNA hybrid substrate (Figure 1A)
Architecture 3 makes it possible for an authorized third party to withdraw metering data directly from the SM with the scope of controlling and scheduling his/her connected
In the present paper, we intend to quantitatively estimate energetic contributions to MT stability, giving a break-down according to the type of physical interaction
These are the aims of the present study. In the following, we first present the theoretical background re- quired to interpret active-DTS experiments before presenting the
(D) WISH assay of cmyb in embryos both with cebpa and dnmt1 homozygote mutation. Note that cmyb was comparable with embryos without dnmt1 homozygote mutation. Red arrows